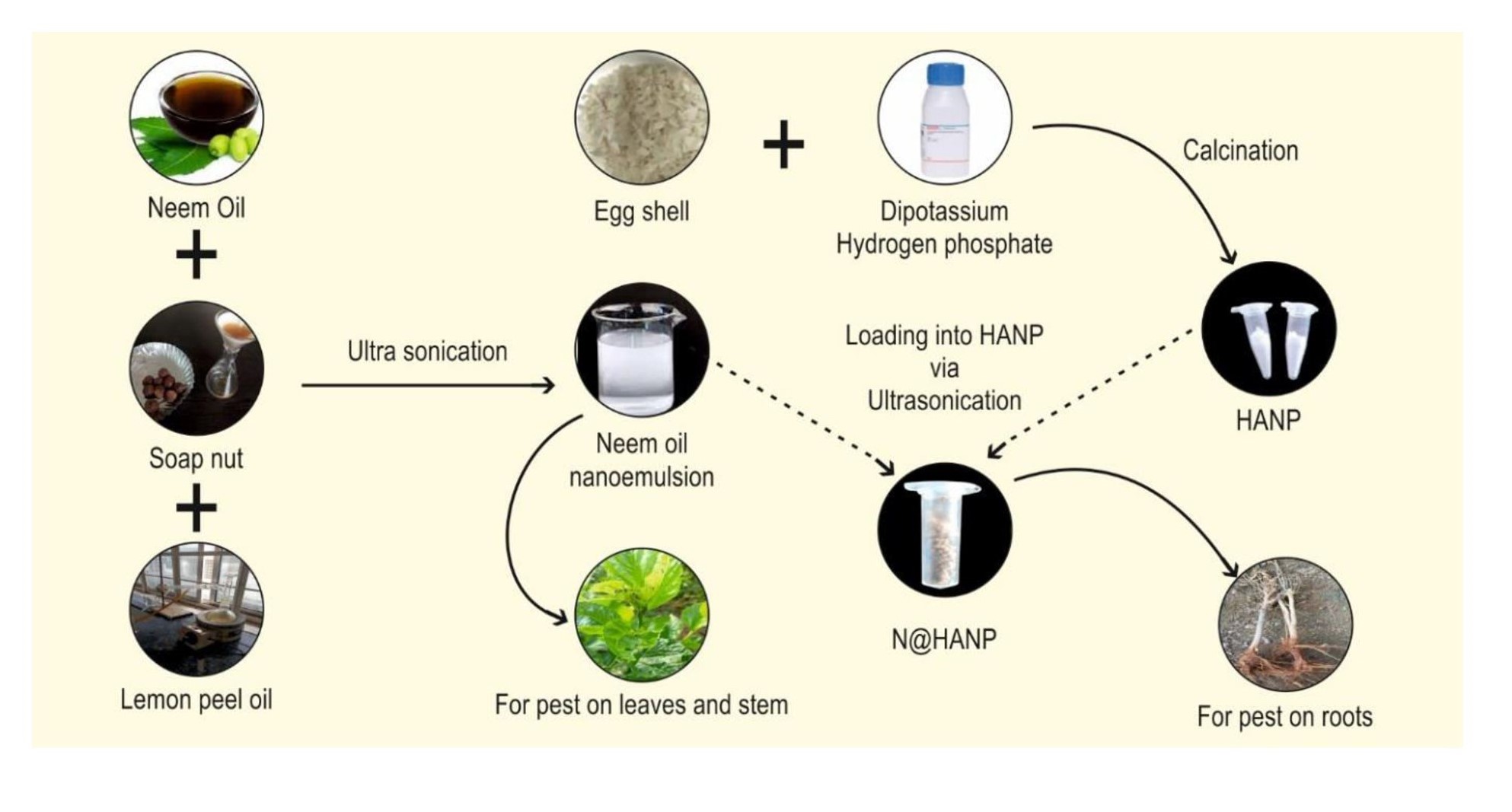
The impact of pests on crop productivity requires an effective and sustainable alternatives to synthetic pesticides, as it pose risks to human health and the environment. The green formulation of a nanoemulsion pesticide by encapsulating into Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles (HANPs) synthesized from waste eggshells is the main aim of this research. The nanoemulsion formulation, containing neem oil (1.75%), lemon peel oil (0.25%), soapnut extract (4%), and water (94%), was prepared using ultrasonication. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) confirmed the high stability of the resulting ~200 nm droplets. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) verified the crystalline nature of HANPs, while Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectral Analysis confirmed successful neem oil presence. In vitro release studies demonstrated an initial burst release (~15% within 5 days), followed by sustained release (~100% by day 70) consistent with Higuchi kinetics (R² = 0.9892). Aphid mortality increased with both time and concentration, reaching complete mortality at 1.75% (v/v) after 12 hours. The LC50 values declined from 1.375% (v/v) at 2 hours to 0.893% (v/v) at 12 hours, indicating enhanced toxicity with prolonged exposure. ANOVA, based on a Box-Behnken design, indicated that neem and lemon peel oil concentrations significantly affected efficacy (p < 0.001). Field trials showed complete Aphid elimination on Solanum lycopersicum, Solanum melongena, and Allium cepa, with no signs of phytotoxicity or harm to non-target organisms.The present study formulates an effective pest control through prolonged delivery of active compounds, offering a cost-effective and environmentally responsible solution for modern agricultural practices.
Total file downloads: 59