- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 16 Downloads
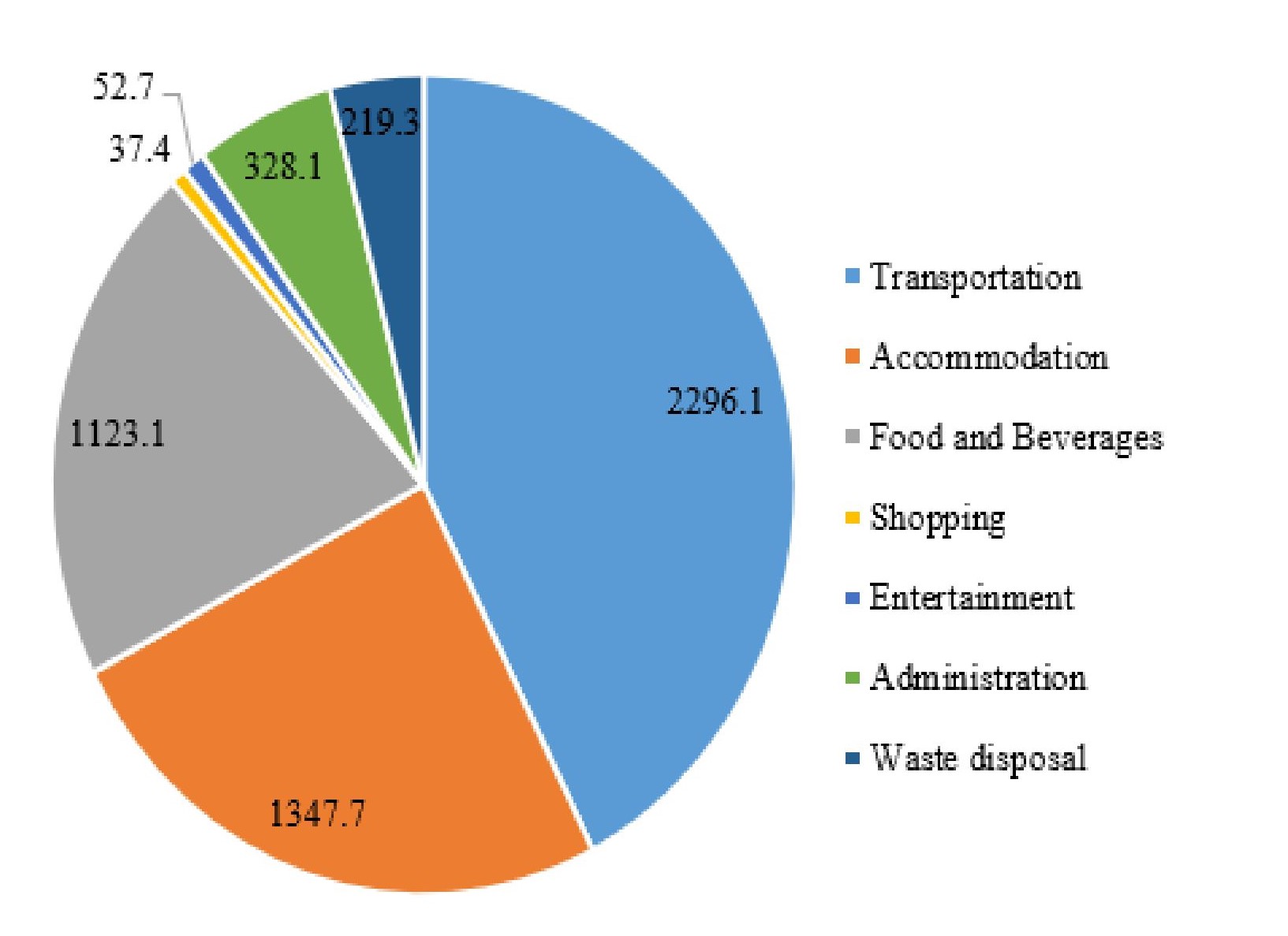
To effectively address the CO2 emissions in the tourism place, in this study focuses a Sanshan scenic spot for precise prediction. The main factors contributing CO2 emission as, accommodation, transportation and catering services which intends to improve the need of carbon emission forecasting methods. To address this issue, we proposed an innovatively integrating the optimization algorithms Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Optimization for accurately predicting the CO2 emissions. Initially, this system taken input from the CO2 emissions occurred from the year of 2010 to 2020. The optimization model contains the input variables, initializing populations, evaluating fitness values, and iterating until convergence to found best prediction model. The experimental results of the proposed PSO-GA system attains 9.86 highest sensitivity showcases best performance in predicting CO2 emissions, as evidenced by its superior Adjusted Rand Index value of 1 after 160 iterations. The predicted and measured values of CO2 emissions using this algorithm remains significant and advanced carbon environment development at scenic spots. The PSO-GA was used to calculate the carbon emissions of three mountainous scenic spots over the next five years, and the medium and high carbon levels should change to a medium carbon development stage by 2024.