- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 10 Downloads
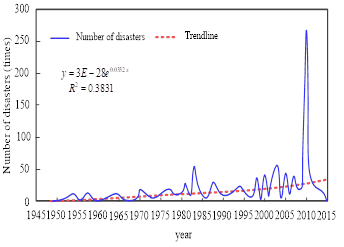
In order to analyze the spatiotemporal change characteristics of regional flood disaster, analyze the main change characteristics and hydrological response of precipitation distribution in Guangxi, and improve the comprehensive utilization efficiency of water resources, this paper introduces the k-means clustering algorithm to design an analysis model of spatiotemporal change characteristics of flood disaster. First of all, obtain the flood data in Guangxi and the observation data of the national meteorological station within 5 km, complete the collection of the basic data of mountain flood disasters. Based on the collected data, an analysis was conducted on the spatial and temporal distribution of flash floods in the Guangxi region. Secondly, the Kriging spatial interpolation method was used to analyze the spatial distribution of precipitation data in Guangxi. The Mann-Kendall trend test was then employed to examine the trend of precipitation-related statistical parameters over time. Additionally, wavelet theory was applied to analyze the time series of annual precipitation and precipitation with different durations in Guangxi. Subsequently, the k-means clustering algorithm was introduced to construct a model for analyzing the spatiotemporal characteristics of flood changes, determining the concentration and duration of precipitation in different years in the region. Finally, analyze the spatiotemporal change characteristics of flood events in different seasons under various indicators, and realize the analysis of flood spatiotemporal change characteristics. The research results indicate that the Frank Copula function fits the best correlation between annual precipitation and temperature, and can better characterize the correlation between the two. The Frank Copula function has the best fitting effect on the correlation between precipitation and temperature in autumn in Guilin, summer in Nanning, and summer and winter in Beihai. In Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, the annual precipitation shows a gradually decreasing trend, especially at R and P stations. In summary, the Frank Copula function can effectively characterize the correlation and trend of precipitation and temperature in different seasons and regions of Guangxi.