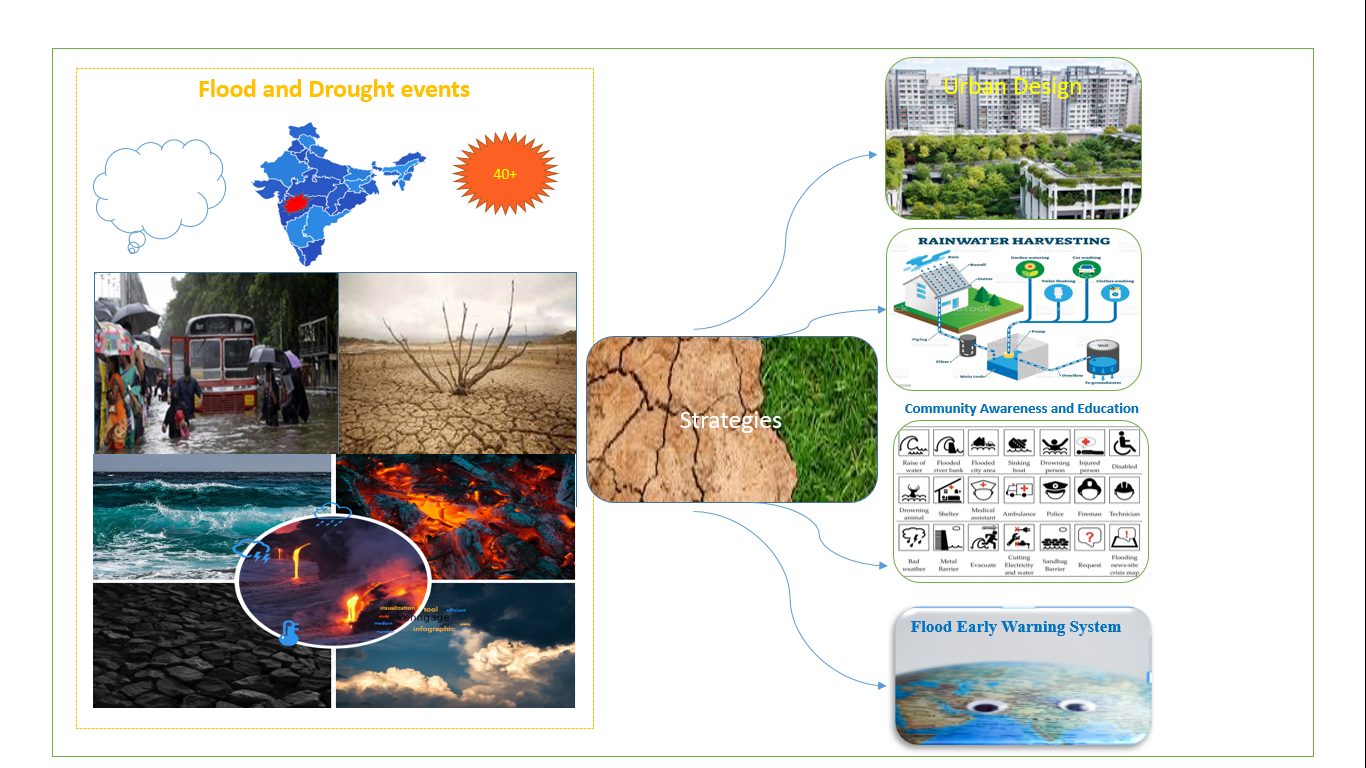
India's droughts and floods, which have affected 8 million hectares yearly since the 1950s, make future adaptation and mitigation plans necessary, as well as an awareness of potential changes. In order to address the growing issues of flood and drought events in urban settings, the study emphasizes the importance of comprehensive water management strategies that ensure both routine water needs and severe event readiness. This study article recommends including drought and flood considerations in building codes and urban planning regulations to boost urban water resilience. The paper provides workable solutions for developing water-sensitive urban design, rainwater collecting, greywater reuse programs, and decentralized water management systems through a collection of case studies and strategy models. It also emphasizes the importance of teaching the population about the dangers of droughts and floods, water conservation methods, and emergency response procedures. The recommendations place a lot of emphasis on the need for a variety of policies that encourage cooperation between stakeholders, including local and state governments, business owners, community leaders, and experts. The policy recommendations include requests for green infrastructure, building standards for flood-resistant homes, water conservation requirements, and climate-responsive legislation, among other subjects. By encouraging sustainable water use behaviors, these concepts aim to increase urban resilience and make cities better prepared to mitigate the consequences of drought and flooding. These recommendations can aid local and state governments in creating a culture of preparedness for catastrophes, protecting communities, and fostering urban water resilience. This case study looks at the intricate relationships between a specific Maharashtrian river's floods, droughts, and water scarcity.
Total file downloads: 65