- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 7 Downloads
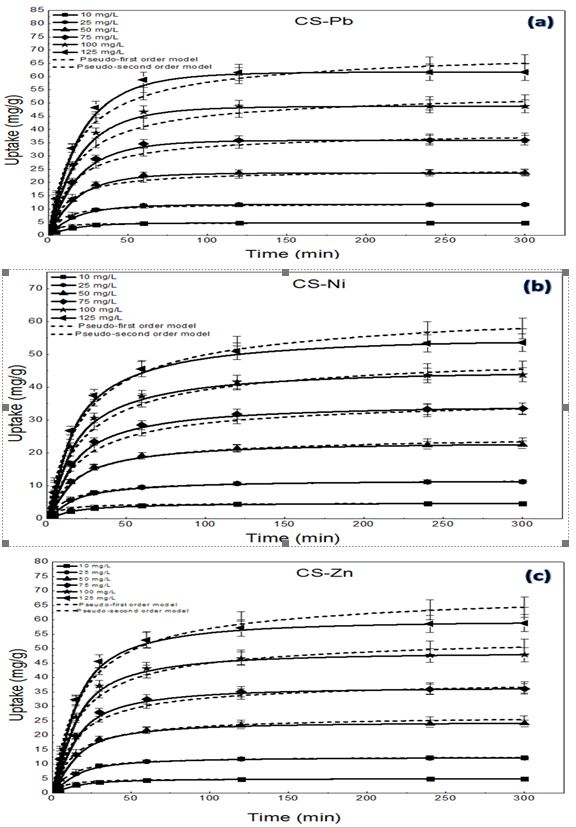
From this study, green seaweed Caulerpa Scalpelliformis is utilized as a sorbent for the removal of three metals such as lead (Pb), nickel (Ni) and zinc (Zn). Adsorption tests showed that maximum removal efficiency of 75.02% for Pb, 80% for Ni and 91.11% for Zn was obtained at an optimal equilibrium pH of 7 for Pb and 6 for Ni, Zn, 2g/L sorbent at an ionic strength of 100 mg/L of 30°C. Four isotherm models, such as Langmuir, Freundlich, Toth, and Sips used in this study to determine the correct fit model from test results. The toth model (R2=0.999) was well fit compared to other isotherms models based on correlation coefficients. Kinetic model results obtained at initial Pb, Ni and Zn concentrations revealed a high biosorption rate. In contrast, the results have been modelled effectively with the pseudo-first and second orders. As a result, tests with elutants found that 0.1M HCl is the perfect desorption elutant for three metal ions.