- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 23 Downloads
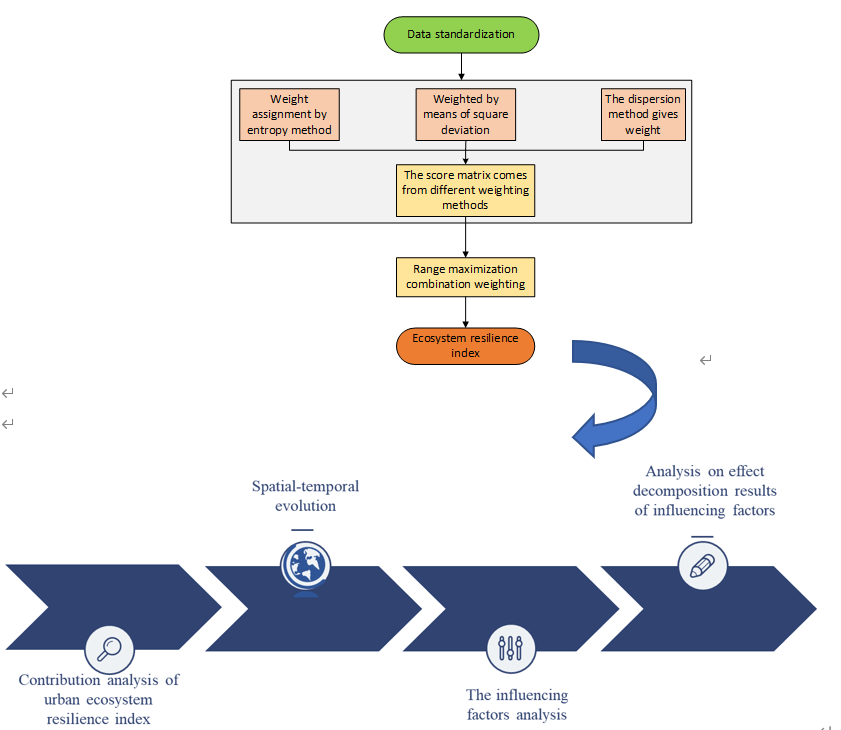
Urban ecosystem resilience is a key concern in the strategy of ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. This paper uses the principle of range maximization to construct an ecosystem resilience index measurement model from the four dimensions of energy, water resources, environment, and economy and society. The spatio-temporal evolution ecosystem resilience of 99 cities in nine provinces of the Yellow River Basin from 2005 to 2019 was analyzed. The spatial econometric model was used to explore the impact of technological innovation, opening to the outside world and industrial structure on the level of ecosystem resilience, so as to provide guidance for improving the level of ecosystem resilience in the Yellow River Basin. The results are concluded as follows: The level of ecosystem resilience in the Yellow River Basin generally increased first, then decreased, and then increased again. The resilience contribution of the environmental subsystem and the economic and social subsystem is relatively large, while the resilience contribution of the water resource subsystem is relatively small. How to improve the resilience level of the water resource subsystem should be considered as a key issue. Scientific and technological innovation, opening to the outside world and industrial structure had obvious spatial impacts on the resilience of the ecosystem in the Yellow River Basin.