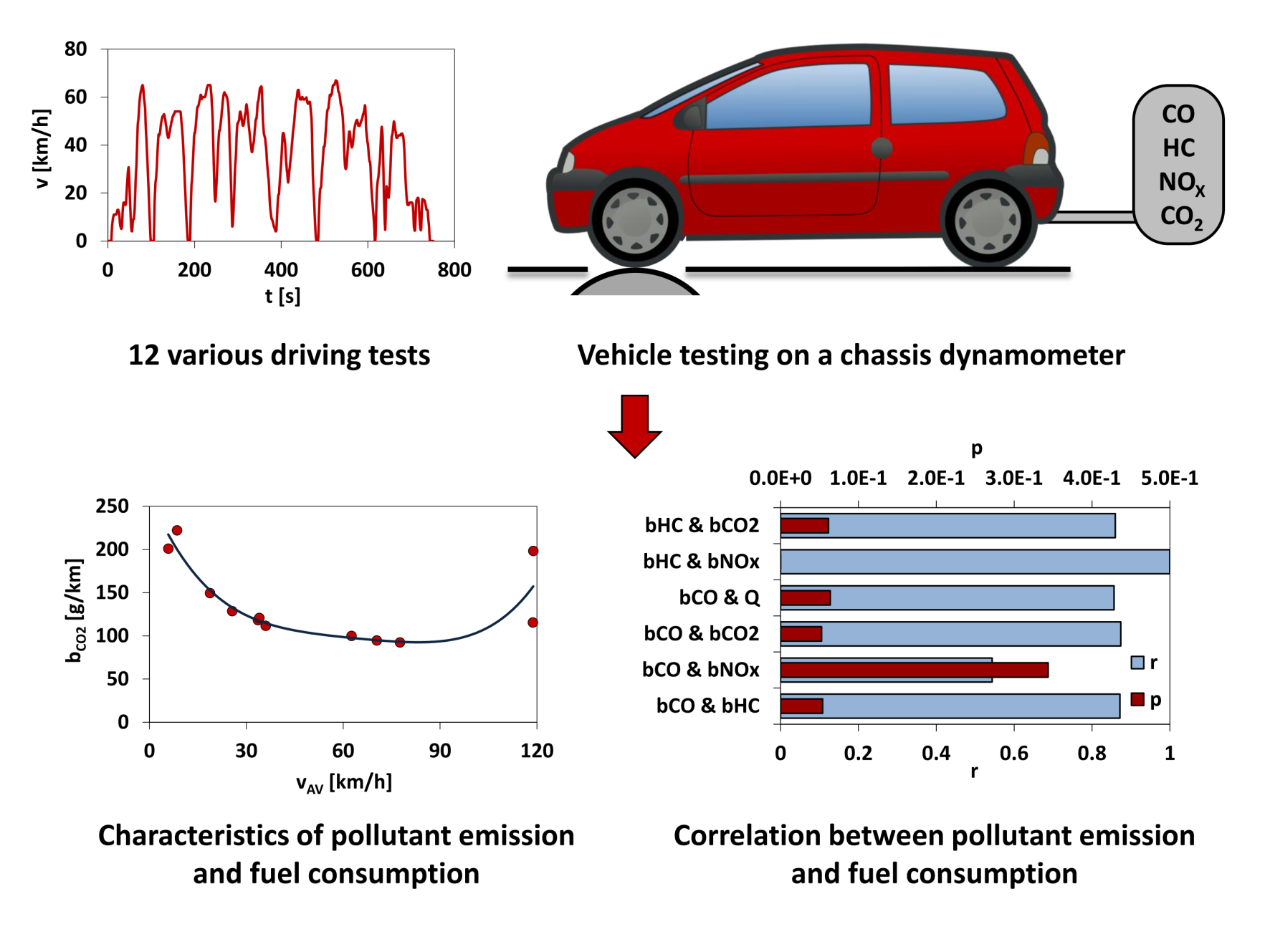
Air pollutant emissions and fuel consumption of vehicles equipped with internal combustion engines are highly susceptible to the conditions of engine operation. The purpose of this research was to investigate the correlation between the emissions of individual pollutants (carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, nitrogen oxides, and carbon dioxide), the fuel consumption and various dynamic conditions of the operation of an engine. The empirical data was obtained by testing of passenger car with a spark-ignition engine on a chassis dynamometer in 12 various driving tests, both type-approval and special. The results indicate, that the strongest correlation exists between the emissions of carbon dioxide and hydrocarbons and between the fuel consumption and the emissions of hydrocarbons and carbon dioxide. The weakest correlation was found to be between the emissions of carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. The average value of vehicle velocity proved to be suitable zero-dimensional characteristic of the dynamic driving conditions. The correlation between the emission of hydrocarbons and the average vehicle velocity can be assessed as the strongest, while between the emission of nitrogen oxides and the average vehicle velocity – the weakest.
Total file downloads: 4