- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 1 Downloads
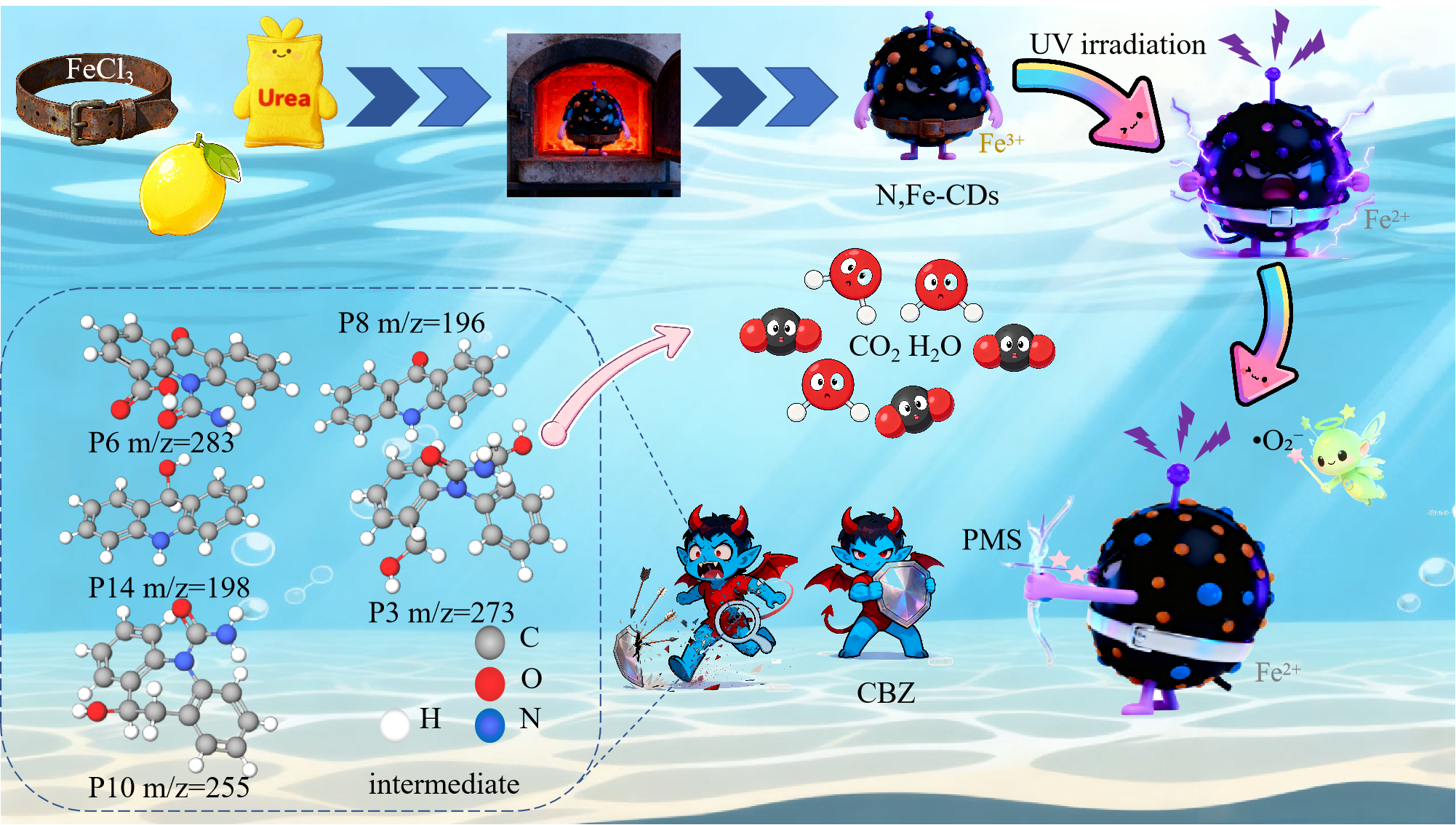
Nitrogen- and iron-co-doped carbon dots (N,Fe-CDs) were synthesized via a hydrothermal method and rationally engineered as a low-iron, UV-responsive catalyst in a UV/N,Fe-CDs/peroxymonosulfate (PMS) system for rapid carbamazepine (CBZ) degradation. Characterization verified a near-spherical morphology, with iron chelation improving light absorption, electron transfer, and catalytic stability.Fe–O, Fe–N, and Fe–OH coordination stabilized Fe species and promoted Fe(III)/Fe(II) redox cycling under UV irradiation through photoinduced electron transfer and ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT). This ensured that the process performed successfully in a large range of PH, between 3 and 9. When the right conditions were met (0.5 mM PMS, 0.10 g/L N,Fe-CDs), 95.4% of the CBZ was removed in 20 minutes, which was 6.8 times faster than UV/PMS. Ions that were present at the same time, like Mg²⁺, NH₄⁺, Cl⁻, and HCO₃⁻ , greatly slowed down degradation. SO₄²⁻ only slowed it down at high concentrations, whereas NO₃⁻ and humic acid had little effect. Mechanistic studies identified 1O₂ and •O₂⁻ as the main species, while SO₄•⁻ and •OH were less important. HPLC-MS/MS found 14 intermediates, and density functional theory calculations pointed to hydroxylation and ring-opening of the seven-membered heterocycle as the main ways these things happen. Predictions of toxicity showed lower risks to the environment. Overall, the UV/N,Fe-CDs/PMS system couples Fe coordination stabilization with UV-assisted PMS activation, suggesting promise for wastewater treatment in complex matrices.