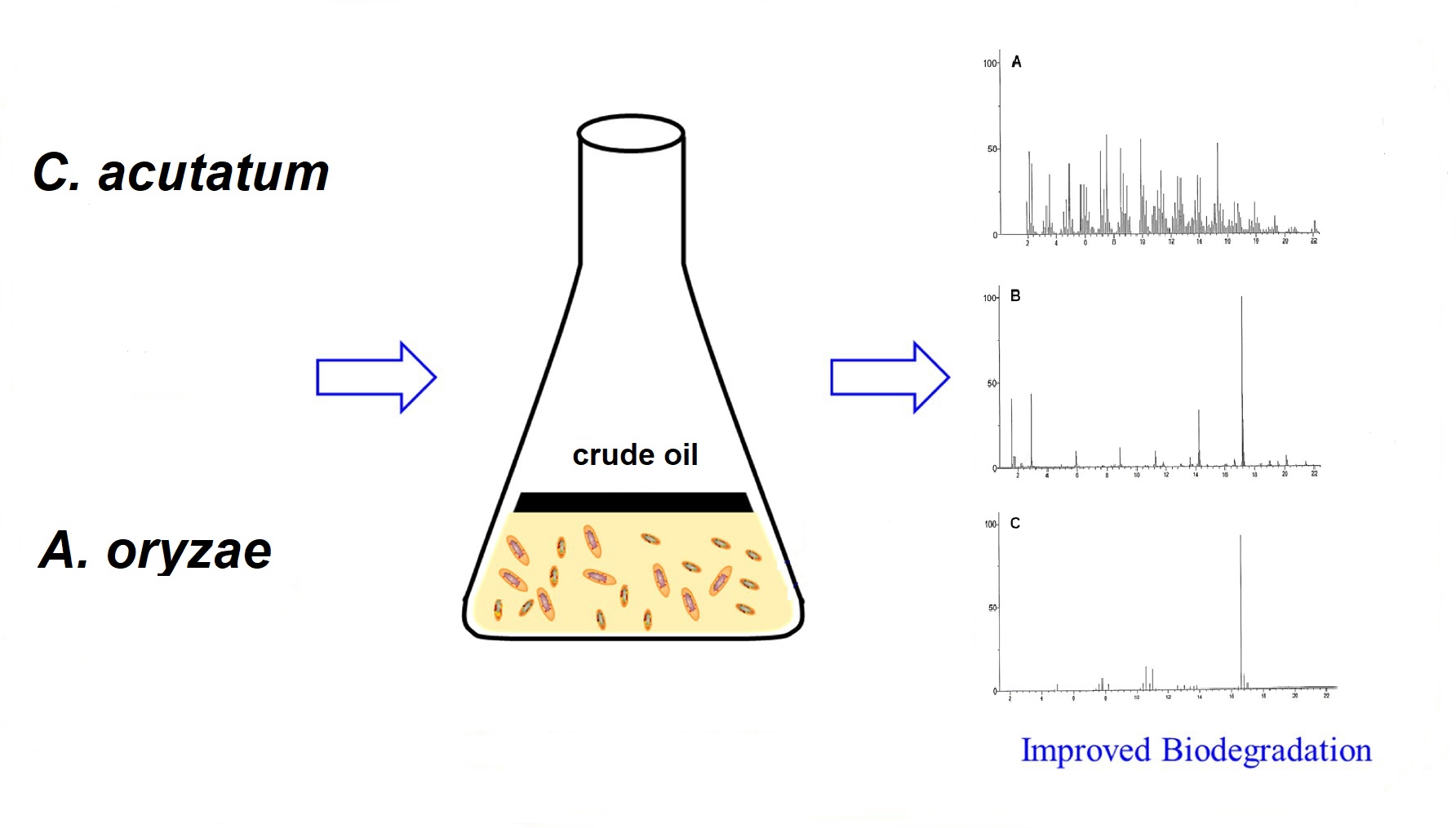
The purpose of the current study was to evaluate endophytic fungi's capacity to break down crude oil. The growth capability of many fungal isolates was investigated using Colletotrichum acutatum and Aspergillus oryzae on a low salt medium with 1% crude oil as the carbon source. As far as we are aware, the isolated species has never been found in contaminated soil samples in Saudi Arabia's eastern area. A. oryzae and C. acutatum have demonstrated their ability to digest crude oil by eliminating 59.7 and 78.1% of it, respectively. It is noteworthy that they were able to lower the surface tension to 50.3 and 40.8 mN/m, respectively. In addition, the hydrophobicity and emulsification activity were found to be 46.7, 54.1, and 41.2, respectively, and 62.4. Zinc sulfate, ammonium sulfate, acid precipitation, and solvent extraction methods were among the recovery assays. These methods all shown a correlation between the amount of biosurfactants and the hydrocarbons under examination. Finally, our research sheds new information on the fungal resources present in terrestrial ecosystems that are continuously contaminated. The safe removal of petroleum-oil contamination, bioremediation, and other industrial applications will benefit from this understanding.