- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 5 Downloads
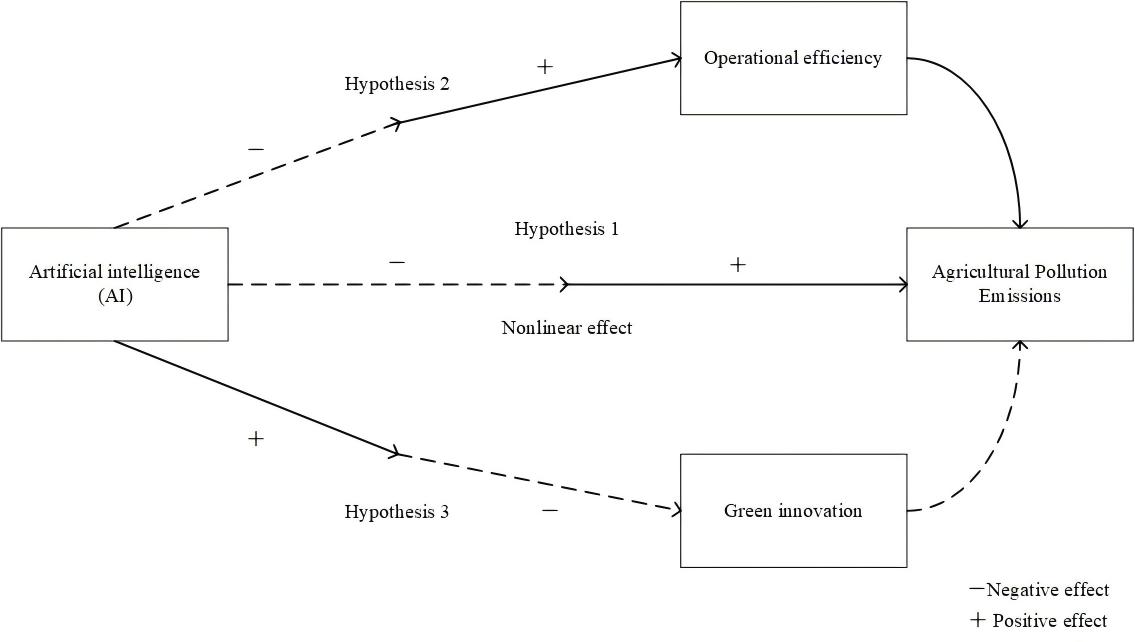
Artificial intelligence (AI) promotes high-quality development in agriculture while also introducing new challenges for the management of pollutant emissions. This study aims to explore the pathways and underlying mechanisms through which AI influences agricultural pollutant emissions. To achieve this, the study employs data from Chinese publicly listed agricultural firms from 2010 to 2022 and conducts an empirical analysis using a semi-parametric additive model. The results show that artificial intelligence has a nonlinear effect on agricultural pollutant emissions, initially inhibiting them and subsequently promoting them. In the early stages of digitalization, constrained by limited resources, AI investment reduces the scale of production, thereby lowering pollutant emissions. However, as AI investment intensifies, firms overcome resource constraints, and the resulting productivity gains and scale expansion effects lead to increased emissions. Mechanism analysis further reveals that AI influences agricultural pollutant emissions through two main channels: it first decreases and then enhances firms’ operational efficiency, and it initially boosts but later weakens their green innovation capacity. These findings provide theoretical support and practical guidance for promoting sustainable development and intelligent transformation in the agricultural sector.