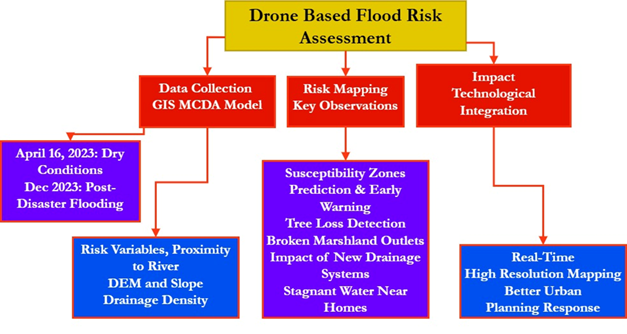
Floods are among the most catastrophic natural disasters because they endanger both lives and assets. The current investigation intends to create a mesoscale state wide flood risk mapping for the district of Chennai in Tamil Nadu, India, utilizing drone data and a GIS-MCDA model. The Chennai cloudburst in 2023 was a catastrophic meteorological disaster that produced considerable floods and devastation, killing more than 50 people. As a result, establishing a flood vulnerability map is vital for managing future catastrophes. In this research, a flood vulnerability map generated using drone technology is utilized to assess damage, create risk susceptibility zone maps, predict disasters, propose mitigation strategies, and manage rescue and rehabilitation efforts. The analysis incorporates key flood risk parameters, including precipitation (60 cm), proximity to the river (2 km), Digital Elevation Model (DEM) elevation (15–20 m), slope (3–8%), Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) categories (e.g., urban, vegetation, water bodies), drainage density (1.5 km/km²), soil type (sandy clay), and lithology (alluvial deposits). From the outcomes of this investigation, policymakers and managers may get more complete insight and precise suggestions about systems for early warning, rescue efforts, and flooding risk mitigation strategies.
Total file downloads: 39