- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 17 Downloads
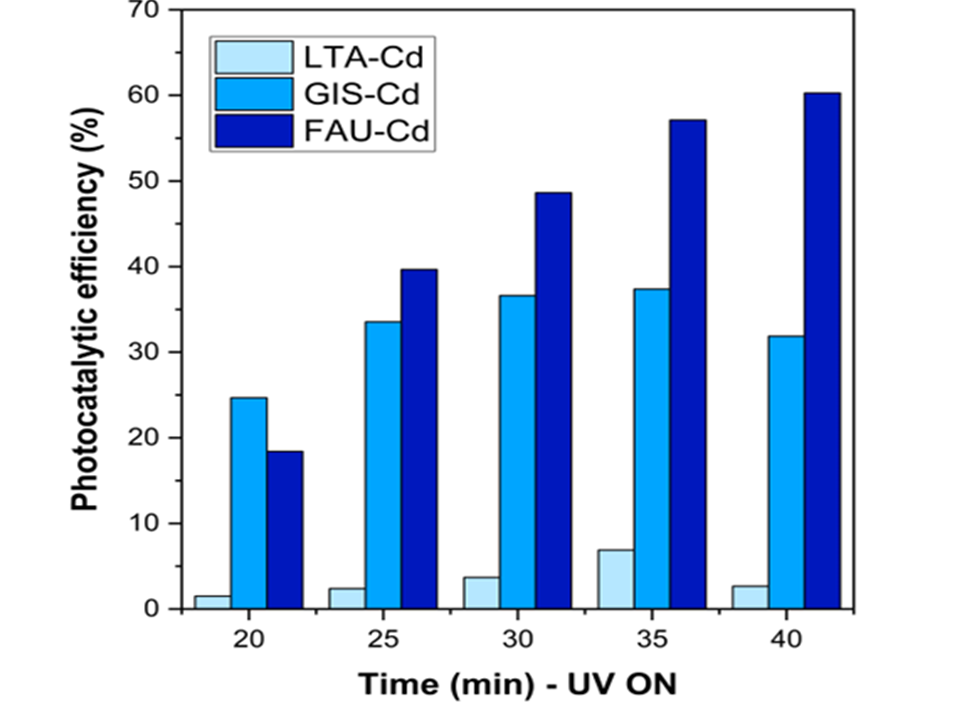
In this study, various types of zeolite support (LTA, GIS-NaP1, and FAU-type Y) were coupled with CdO active sites to develop effective photocatalysts for volatile organic compounds (VOC) treatment (isopropanol as a model). Notably, both LTA-Cd and FAU-Cd samples retained the structure of the original zeolite, as indicated by the presence of characteristic peaks in their X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns, whereas the transformation was seen in GIS-Cd sample. Cadmium oxide formation and distribution on the catalyst's surface were confirmed through XRD analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images, and three-point energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) mapping. When comparing the efficacy in treating isopropyl alcohol (IPA) among the samples, FAU-Cd exhibited the best performance, containing only 1.59% of cadmium element. Interestingly, the variation in moisture stream ratio had minimal impact on IPA adsorption capacity, and its effect on the photocatalytic activity of the FAU-Cd sample could be negligible. It suggests that FAU-Cd holds promise as an effective photocatalyst for environmental cleanup purposes.