- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 5 Downloads
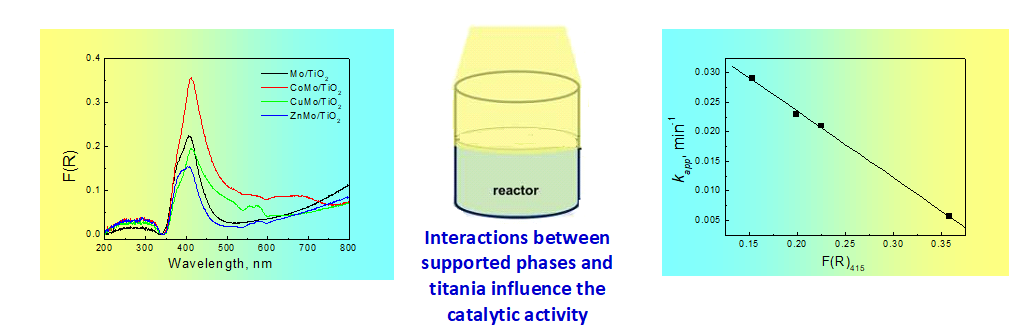
TiO2 is the most effective photocatalyst but it has low adsorption in the visible region. Many efforts have been done to improve its photocatalytic activity in the solar region. In this study we use Mo-oxy species supported on titania surface since it is well known that titania surface can dispersed Mo oxo species through the development of intense interactions. The binary system was further modified with another metal ion M2+ (M: Co, Cu, Zn). These ions have different chemical properties and they alter the physicochemical properties of the ternary system. The photocatalytic activity of the prepared catalysts were determined for the degradation of 0.5 mg L-1 sulfamethoxazole under solar irradiation. It was found that the deposition of Mo has a detrimental effect on the activity of TiO2 while the deposition of Zn or Cu can improve the activity of the ternary system. The sulfamethoxazole degradation follows first order kinetics and the activity of the catalysts is well correlated with the interactions developed between support and supported phases.