- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 6 Downloads
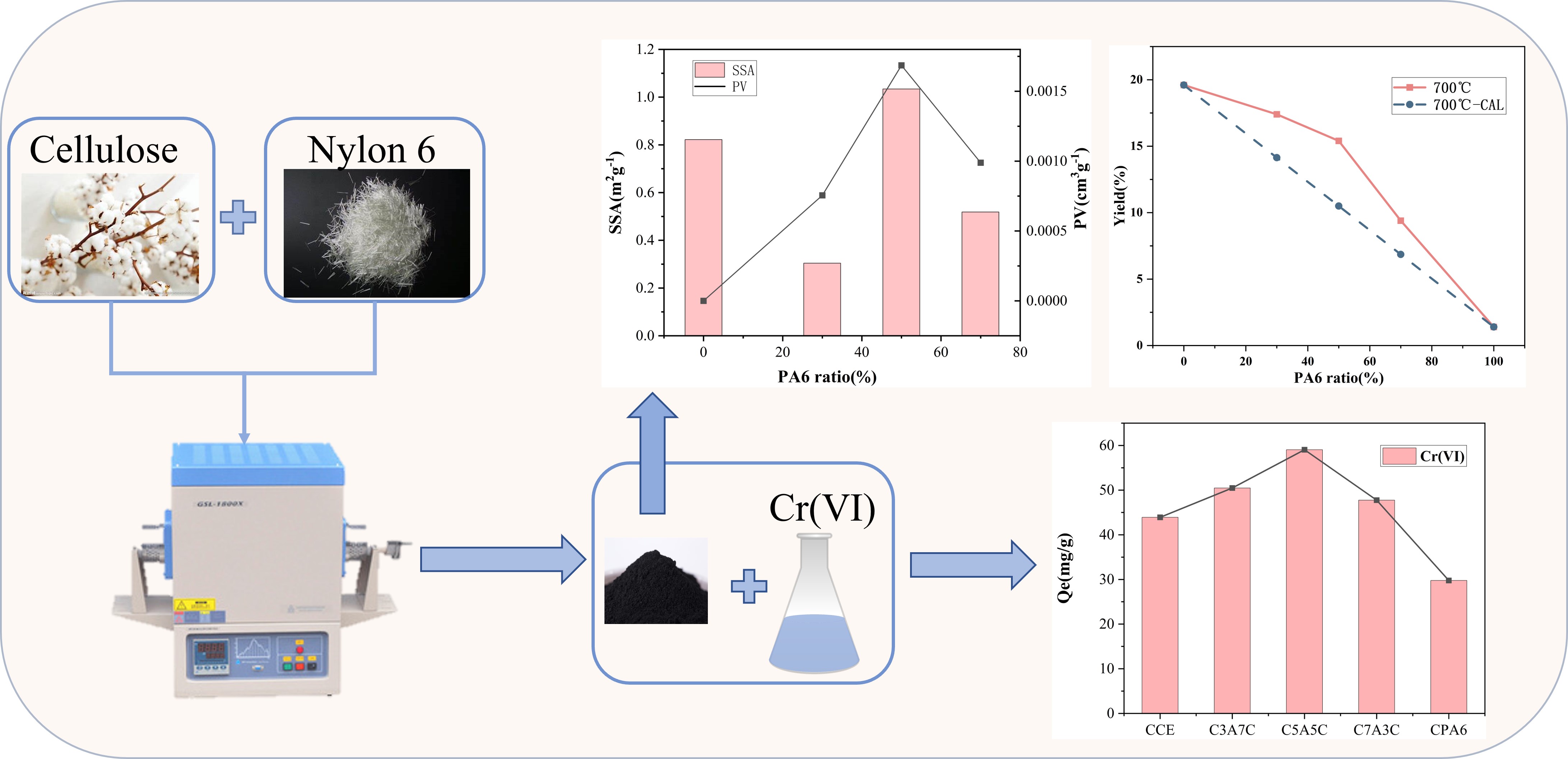
Recycling of used textiles is an important part of achieving sustainable development and low carbon, which can effectively alleviate environmental pollution and improve waste reuse, but the recycling management of blended textiles is particularly challenging. Nylon6 and cotton blends are gaining popularity as high-value-added fabrics in the market, but the issue of recycling and disposal has yet to be resolved. Cotton and polyamide 6 at varying weight percentages were co-pyrolyzed in this study, and the co-pyrolysis process was evaluated using a Synchronized Thermal Analyzer (TG-DSC) to determine the synergistic effect of the two. The synergistic effect greatly contributes to the output of charcoal, increasing the specific surface area and pore volume of charcoal, thus enhancing the adsorption capacity of charcoal for Cr (Ⅵ); when the polyamide 6 ratio is 50%, the char has the highest adsorption capacity on Cr (Ⅵ). The physicochemical features of co-pyrolytic char were investigated using SEM-EDS, XPS, BET, and FTIR to determine the synergistic mechanism. Overall, cotton and polyamide 6 exhibit apparent synergy in the co-pyrolysis process, providing char with extraordinary adsorption capability.