- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 26 Downloads
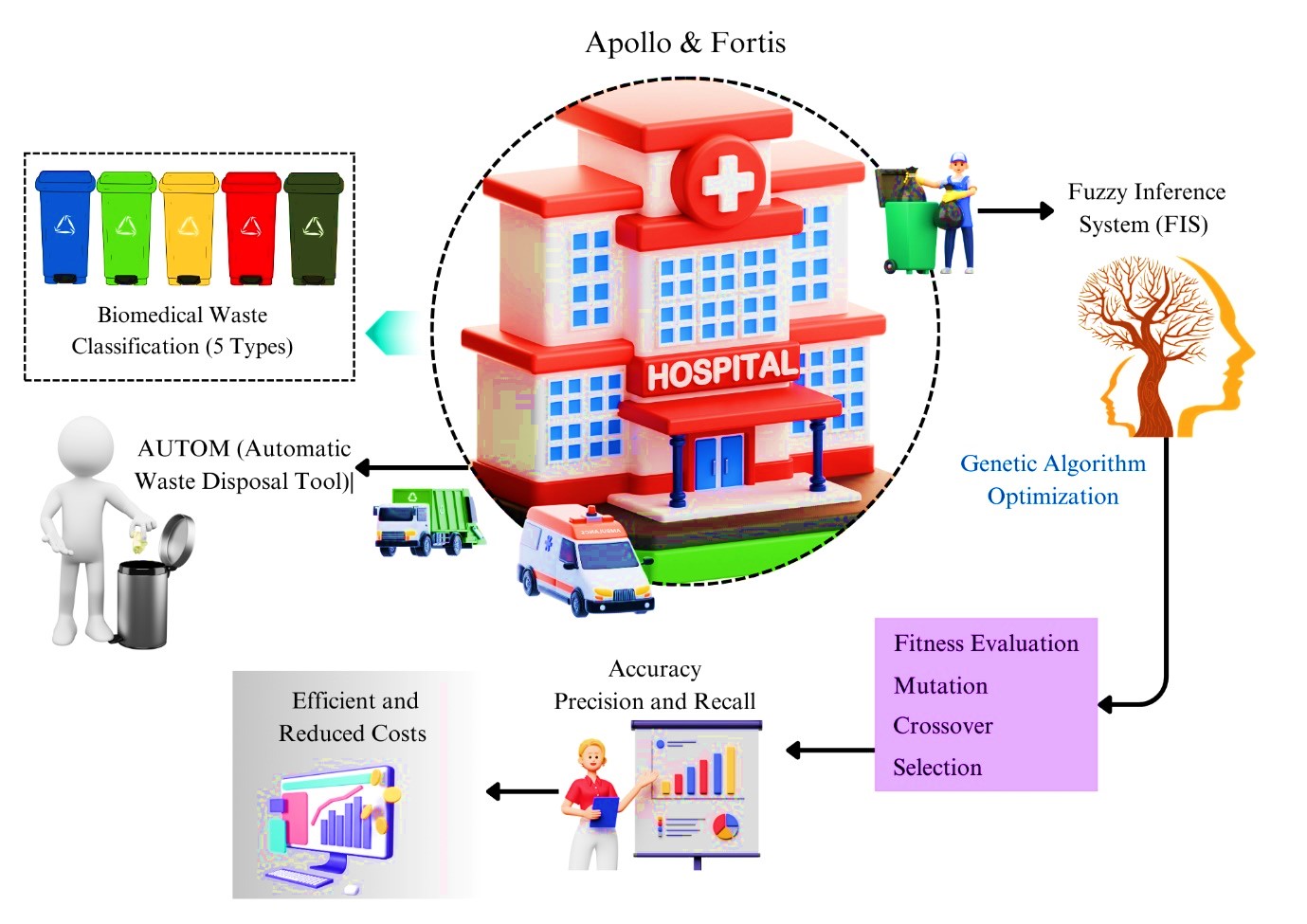
Efficient biomedical waste management is essential for hospital hygiene and public health, particularly within the context of smart city infrastructures. This study proposes an innovative hybrid model combining a Genetic Algorithm (GA) with a Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) to enhance waste classification accuracy and improve segregation efficiency. Leveraging six months of empirical data from Apollo Hospitals and Fortis Malar Hospital in Chennai, the model is tailored to classify five distinct types of biomedical waste effectively. A central component, AUTOM, employs fuzzy logic for automated decision-making, optimizing waste disposal and addressing challenges like the preservation of critical genetic information typically compromised in traditional GA approaches. This integration not only improves system interpretability but also enables precise waste classification using compact, cost-effective sensors that ensure scalability. Validation in the Proteus simulator demonstrates robust performance, with the model achieving a classification accuracy of 96.4%, precision of 96.8%, and recall of 94.8%. These results underscore the GA-FIS model's potential to elevate biomedical waste management practices, contributing to sustainable public health efforts and environmental protection within smart cities.