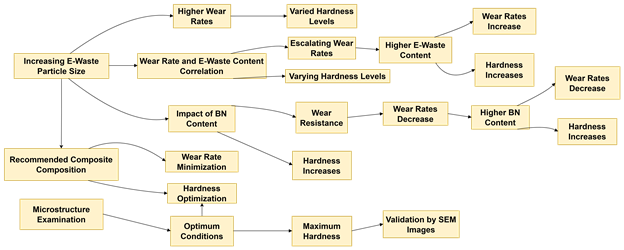
This study examines the properties of Mg (Magnesium)/Electronic Waste/BN ( 10.0pt;line-height:200%;mso-ansi-language:EN-US;mso-bidi-font-weight:bold">Boron Nitride) composite materials by analyzing their wear rate and hardness using a one-variable-at-a-time approach. It reveals intricate relationships affecting material performance, with increasing E-Waste particle size causing higher wear rates and varying hardness levels. E(Electronic EN-US">)-Waste particle size increases wear rates, ranging from 0.62 to 1.18 ×10-2 mm3/m, correlating with size increments. Hardness values range from 32 to 51 HRB, varying with particle size. Wear rate and E-Waste content directly correlate, with higher E-Waste content escalating wear rates from 0.69 to 1.23 ×10-2 mm3/m and hardness increasing from 31 to 44 RHB. The weight percentage of BN significantly impacts wear resistance, with wear rates decreasing with higher BN content. Hardness increases from 42 to 47 RHB ( line-height:200%;mso-ansi-language:EN-US;mso-bidi-font-weight:bold">Rockwell Hardness Scale B) with a higher BN content. A 10 µm size of 5 wt.% of e-waste with 1 wt.% of BN mixed composite is recommended to minimize the wear rate (0.61 ×10-2 mm3/m) of the composite. The microstructure of the worn-out surfaces under optimum conditions is examined. The maximum hardness (52 RHB) has been obtained by mixing 30 µm of 10 wt.% of e-waste with 3 wt.% of BN particles in a mixed composite. The microstructure of the worn-out surface is validated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images.
Total file downloads: 12