- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 15 Downloads
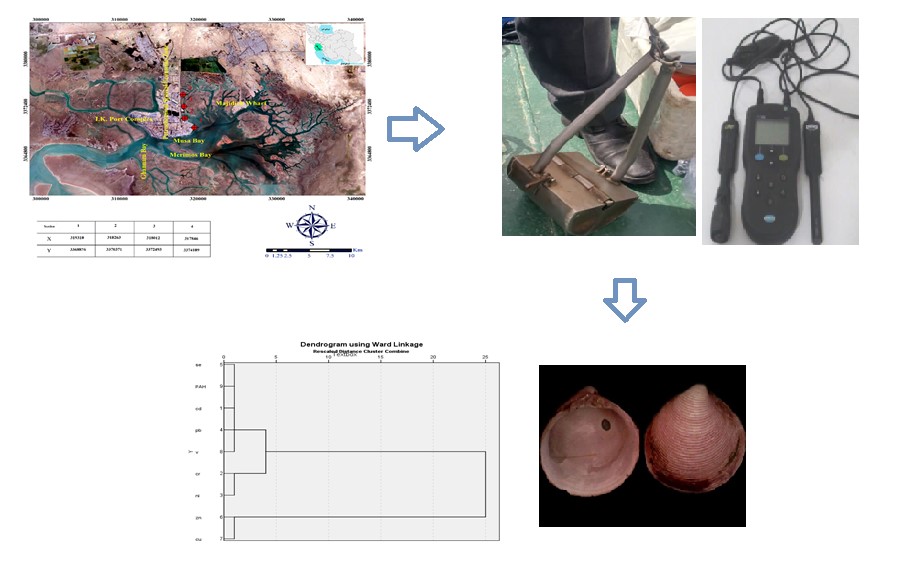
This study evaluates the contamination levels of heavy metals and petroleum hydrocarbons in Jafari Creek sediments and the effect of these pollutions on Macrobenthos in 2017. Studies to understand the effect of heavy metal Cadmium, Chromium, Nickel, Lead, Selenium, Zinc, Copper, and Vanadium, and 16 hydrocarbon compounds, organic material, and soil texture on the population of Jafari Creek Macrobenthos in five stations along the estuary and analyzed using standard procedures. The 4 identified Macrobenthos included Bivalvia with 9 species, Gastropoda with 8 species, Crustacea with 7 species, and Polychaeta with 6 species totaling Macrobenthos 3645.14 per square meter. The dominant class was Polychaetes (53.9%), followed by Bivalvia (23.2%), Gastropoda (9.93%), and Crustaceans (15.8%), with slightly different (P<0.05), were in the second and third class. Among the studied metals, zinc, chromium, and nickel had the highest concentration. Among the hydrocarbons, Anthracene at station 1, Fluorene at station 2, Phenanthrene and Dibenzo [A, H] Anthracene at station 3, and Fluoranthene at station 4 with a concentration between <0.01- 0.091 ppm had the highest value. The highest and lowest heavy metal concentrations were measured at station 4 (215.54 ± 14.58 ppm) and station 1 (102.39 ± 24.15 ppm), respectively. In return, stations 1 (0.339 ± 0.074 ppm) and 4 (0.196 ± 0.078 ppm) had the highest and lowest concentration of hydrocarbons, respectively. Regarding the number of identified Macrobenthos, stations 3 and 2, with 1738.64 and 333.28 n/m2 had the highest and lowest numbers, respectively. The class of Crustacea had a positive correlation with zinc, copper, and lead metal and a negative correlation with Selenium. Polychaeta was positively correlated with cadmium and vanadium. Gastropoda had a negative correlation with vanadium and chromium, a positive correlation with lead and hydrocarbons, and Bivalvia correlated negatively with lead and zinc and had a correlation with vanadium. Considering that the areas around Jafari Creek are an industrial, petrochemical, and economic region considered one of the important catchments in the province of Khuzestan, the sediments, water, and animal tissues must be periodically the analysis of heavy metals and oil hydrocarbons should be considered.