- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 3 Downloads
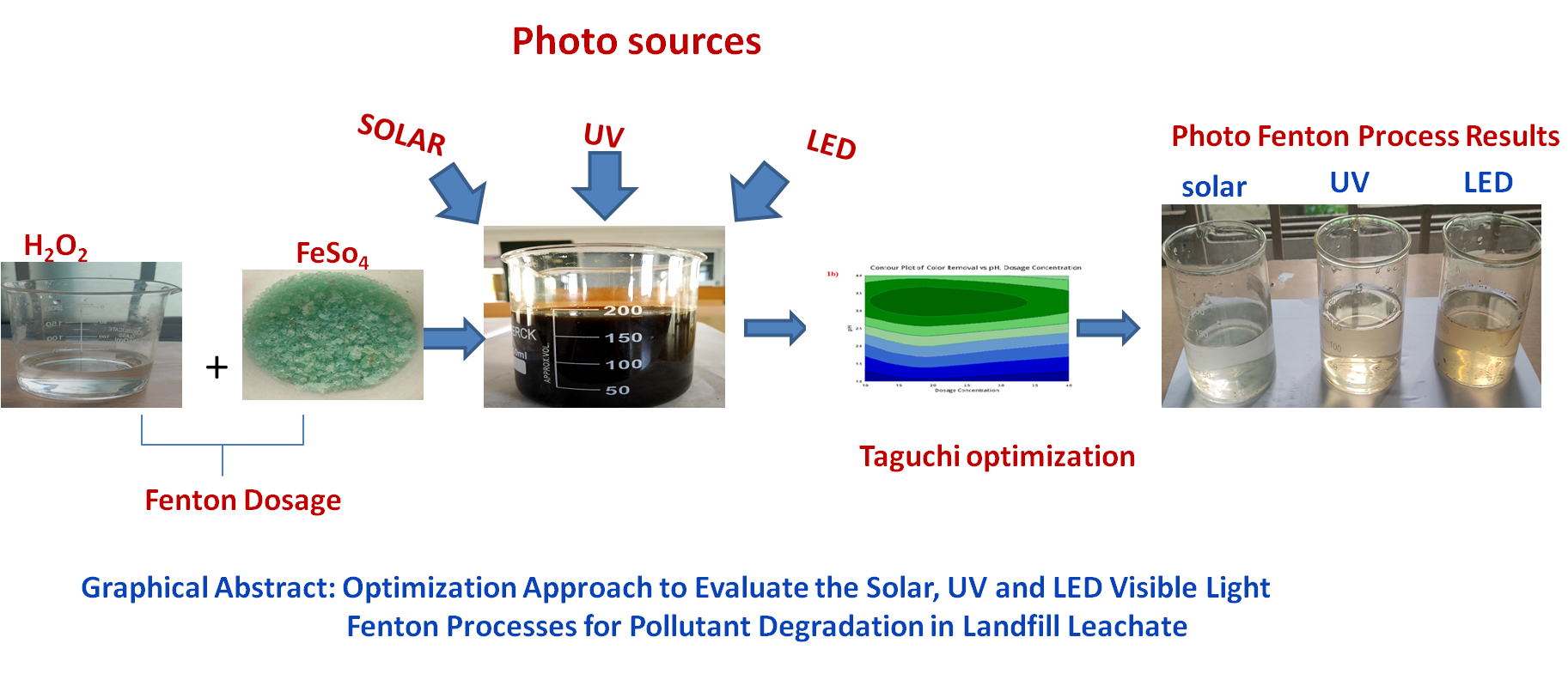
In the current study, three different photo-assisted sources were used to evaluate the photo-Fenton oxidation process for the pollutant degradation of mature landfill leachate. Solar, UV, and LED visible light photo sources were adopted in this Fenton process. Fenton dosages (FeSO4 : H2O2) 1:30, 1.5:30, 2:30, and 2.5:30g/L were used in the investigation, which was conducted under a variety of pH settings (2 to 3.5) and at experimental reaction duration of 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes. To analyze and compare the efficiency of the solar, UV, and LED visible light photo Fenton processes for pollutant degradation, Taguchi experimental design orthogonal arrays (L16) was employed. To analyse the significance of this experimental design for landfill leachate treatment, Larger the Better was selected. The highest levels of pollutant degradation in the Solar Photo Fenton method was identified when compared to UV, and LED visible light photo Fenton processes. The maximum removal of 95% color, 83% COD, 89% TSS, 94% Cr, 86% Cd, and 93% Cu was achieved in Solar Photo Fenton process at pH-3, Fenton dosage 1.5:30 g/L and reaction period 60 minutes.