- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 3 Downloads
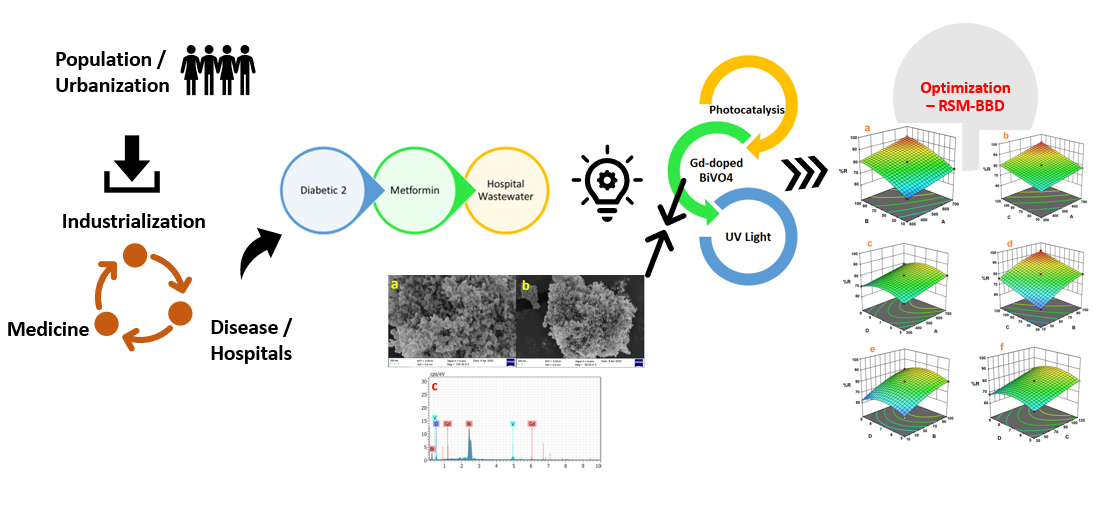
This study aimed to synthesize Gadolinium-doped Bismuth Vanadate (Gd-BV) using co-precipitation and evaluate its effectiveness in removing metformin from hospital wastewater and also optimization done using Response Surface Methodology (RSM), specifically a Box-Behnken Design (BBD). A 5% Gd-doped BV photocatalyst was prepared and tested for metformin removal under UV light. The RSM-BBD approach, implemented with DesignExpert software, explored the impact of initial metformin concentration (300-700 mg/L), Gd-BV dosage (10-100 mg), reaction time (30-120 min), and pH (5-9). The optimal conditions identified resulted in a 92.273% removal efficiency for metformin, achieved with an initial concentration of 595.730 mg/L, a catalyst dosage of 88.404 mg, a reaction time of 115.650 min, and a pH of 7.778. Removal of metformin shows better efficiency of 92.273%.