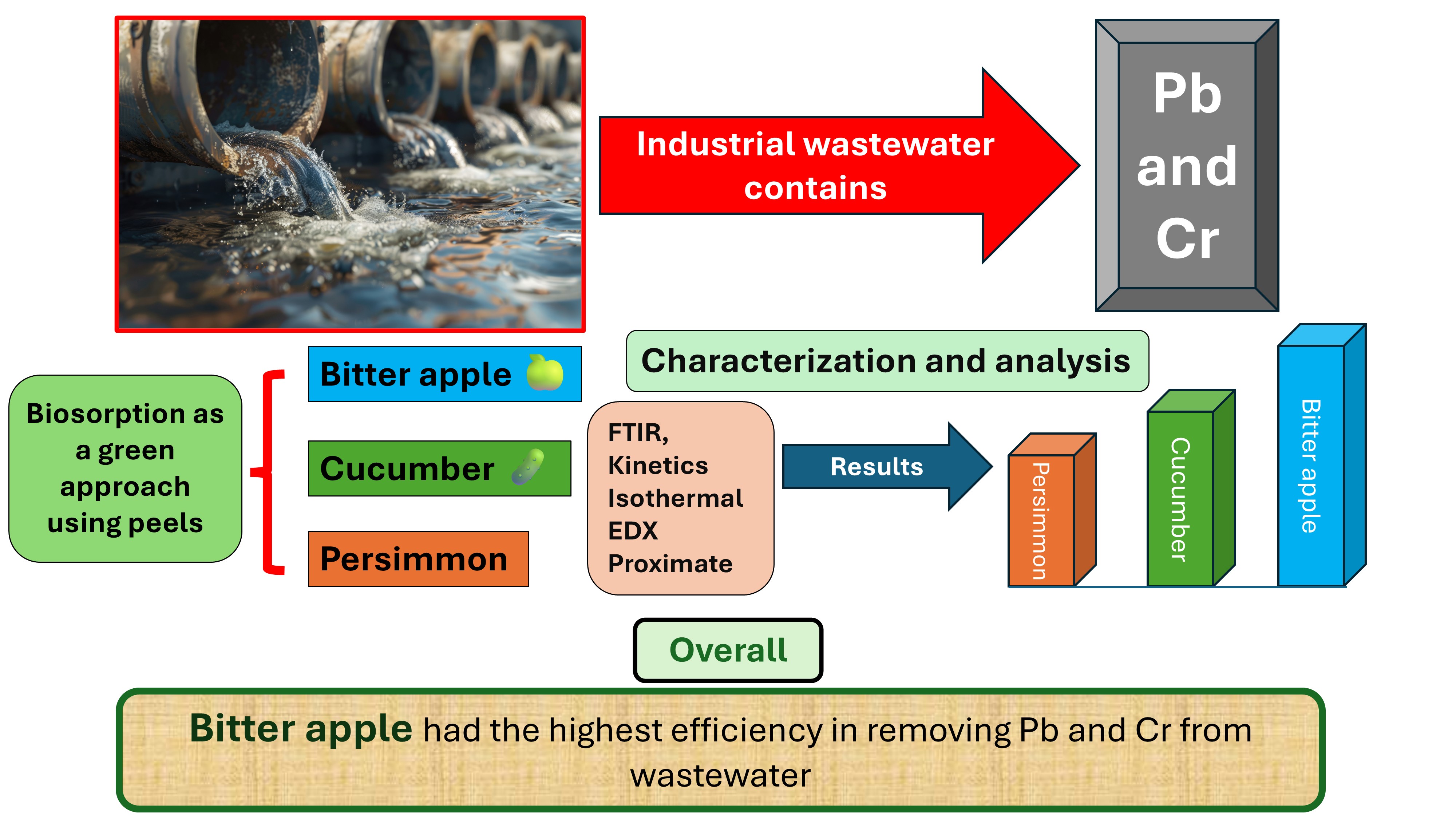
This study explores the efficacy of plant-derived biosorbents - bitter apple, persimmon, and cucumber peels – as a green chemistry solution for the removal of toxic heavy metals, specifically lead (Pb) and chromium (Cr), from sewage water collected from Harnoli and Piplan, Pakistan. Batch biosorption experiments were conducted using biosorbent doses of 1, 2, and 3 g L-1 at contact times of 24 and 48 hours. Heavy metal concentrations were measured using Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS), and results were statistically validated through one-way ANOVA (Pb: F(5,30) = 18.42, p < 0.001; Cr: F(5,30) = 16.89, p < 0.001), followed by Duncan’s multiple range test. Biosorption efficiency increased proportionally with biosorbent dose and contact time. Bitter apple peels at 3 g for 48 h achieved the highest removal in Piplan samples, reducing Pb from 0.64 to 0.14 ppm and Cr from 0.41 to 0.10 ppm. The reduction in the concentration of Pb and Cr using bitter apple peels was 78.1 and 75.6%, respectively, in comparison to the control. Persimmon showed similarly high performance (Pb: 0.24 ppm; Cr: 0.16 ppm), while cucumber peels, although less efficient, still achieved meaningful Pb removal. FTIR analysis confirmed the presence of hydroxyl, carboxyl, and carbonyl groups responsible for metal binding via ion exchange and complexation. Notably, a selective adsorption trend was observed, with higher affinity for Pb than Cr across all biosorbents, which highlights the practical applicability of agro-waste biosorbents in low-cost wastewater treatment technologies.
Total file downloads: 4