- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 8 Downloads
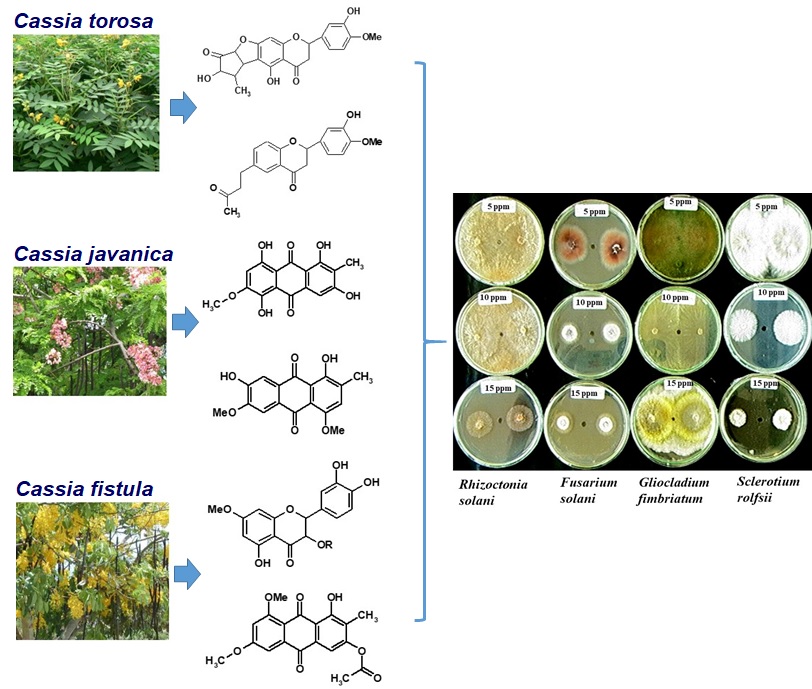
The Cassia plant has several species which are spread throughout the whole of Indonesia. The three types of Cassia are Cassia torosa, Cassia javanica and Cassia fistula L, has been used traditionally by the community for treatment and biofungicides. Therefore this study has a great opportunity to obtain bioactive compounds that have strong activity as anti-pathogenic fungi. This study aims to analyze the extent of the activity of flavonoid and anthraquinone compounds from Cassia sp against pathogenic fungi. The methods in this research include isolation of secondary metabolites (flavonoids and anthraquinone compounds from Cassia sp), manufacture of fungus growth media, culture of fungi, testing of flavonoids and anthraquinone activity from Cassia sp againts fungi and identification of it's activity against fungi. In this study three flavonoid compounds and three anthraquinone compounds from Cassia sp were isolated, namely Torosflavone C and Torosflavone D (from Cassia torosa), 1,3,5,8-tetrahidroxy-6-methoxy-2-methylanthraquinone and 1,7-dihydroxy-4,6-dimethoxy-2-methylanthraquinone (from Cassia javanica), Rhametin-3-O-Gentiobioside and 1-hydroxy-3-ethanoate-6,8-dimethoxy-2-methylanthraquinone (from Cassia fistula). In testing the anti-fungal activity of those compounds against several pathogenic fungi plants showed that Torosflavone D with a concentration of 5 ppm was the most effective percentage of inhibition, because it can inhibit the growth of the Fusarium oxysporum fsp. lycopersici (= 48.75%), followed by the compound 1-hydroxy-3-etanoate-6,8-dimethoxy-2-methylanthraquinone at a concentration of 5 ppm can inhibit the growth of the fungus colonies of Rhizoctonia solani (= 40.20%) . Cassia sp can be used as a source of biological anti-fungus and can help the community to cope with plant diseases caused by fungi.