- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 30 Downloads
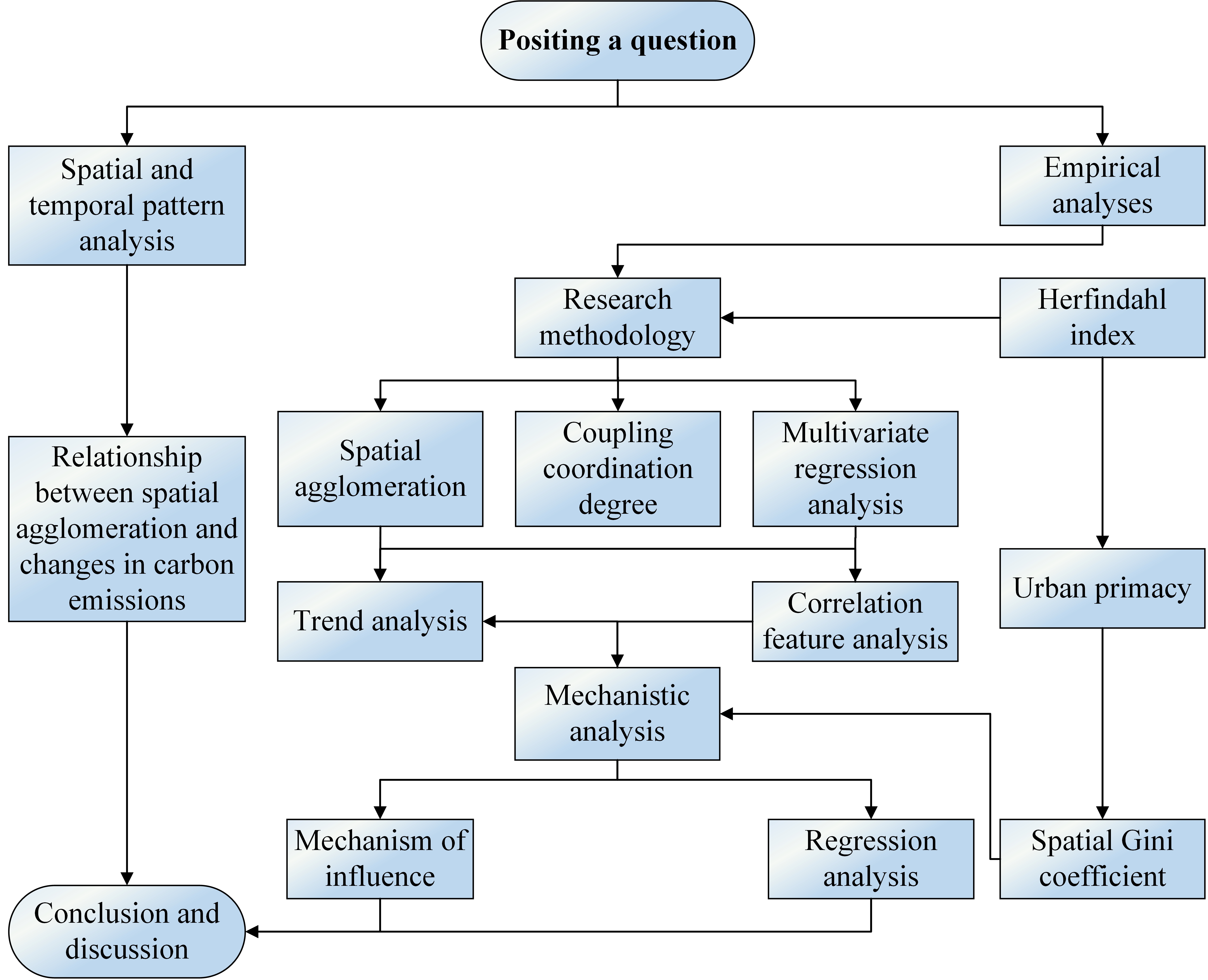
Elucidating the mechanism of the correlation between urban spatial agglomeration processes and carbon emission levels can provide valuable scientific underpinnings for town planning under the constraints of low-carbon goals. This study investigates the characteristics of urban spatial agglomeration in Jilin Province and its association with carbon emission levels. This is achieved by constructing spatial agglomeration indicators, and multiple linear regression models. The findings are as follows: (1) Over the period from 2004 to 2020, the overall trend of urban spatial agglomeration in Jilin Province was characterized by an initial decline, followed by a subsequent increase, but ultimately rising as a whole. (2) A significant negative correlation exists between urban spatial agglomeration and carbon emission levels. Spatial agglomeration in towns exerted a strong influence on changes in regional carbon emission levels.. Specifically, spatial clustering in service industries demonstrated a more pronounced impact on carbon emissions than was the case in production sectors. (3) A regression analysis reveals that the spatial agglomeration of urban population and economic factors has a significant negative impact on both total carbon emissions and carbon emission intensity. The spatial concentration of urban populations is found to have a marked influence in enhancing carbon emission efficiency.