- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 72 Downloads
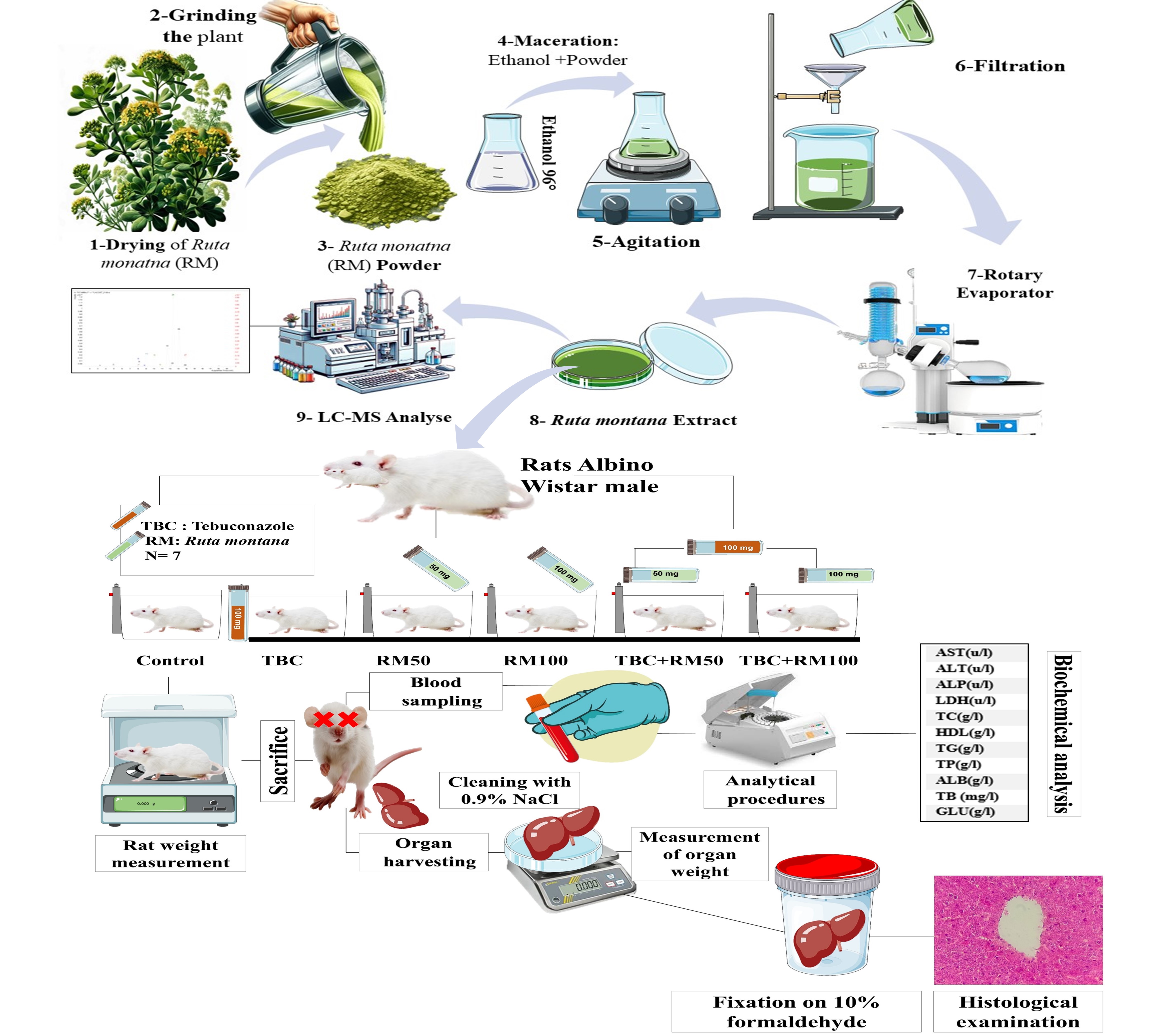
In this investigation, we assessed the phytochemical composition and hepatoprotective properties of Ruta montana, a plant indigenous to Algeria, against liver damage provoked by the systemic fungicide tebuconazole in male Wistar rats. We distributed forty-two rats, each weighing an average of 178±67.2 g, into six groups consisting of seven animals each. The first group, serving as the control, received no intervention. The second group underwent treatment with tebuconazole at a concentration of 100 mg/kg. The third and fourth groups were treated with Ruta montana extracts at dosages of 50 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg, respectively. The fifth and sixth groups received combined treatments of tebuconazole (100 mg/kg) and Ruta montana extracts at 50 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg, respectively. Over a period of 50 days, we administered these treatments via oral gavage. The ethanolic extract of Ruta montana, prepared through maceration, underwent analysis using LC-MS/MS, which revealed the presence of nine significant phenolic compounds. The findings demonstrate that exposure to tebuconazole significantly decreased both body and liver weights, and notably altered levels of hepatic enzymes (AST, ALT), indicative of liver toxicity. In contrast, treatment with Ruta montana extract ameliorated these adverse effects, confirming its protective efficacy. Histopathological examinations further substantiated the amelioration of liver tissue damage in rats receiving the plant extract. This research underscores the significant role of bioactive phenolic compounds in Ruta montana in mitigating hepatic injuries induced by tebuconazole, thereby highlighting its potential therapeutic benefits.