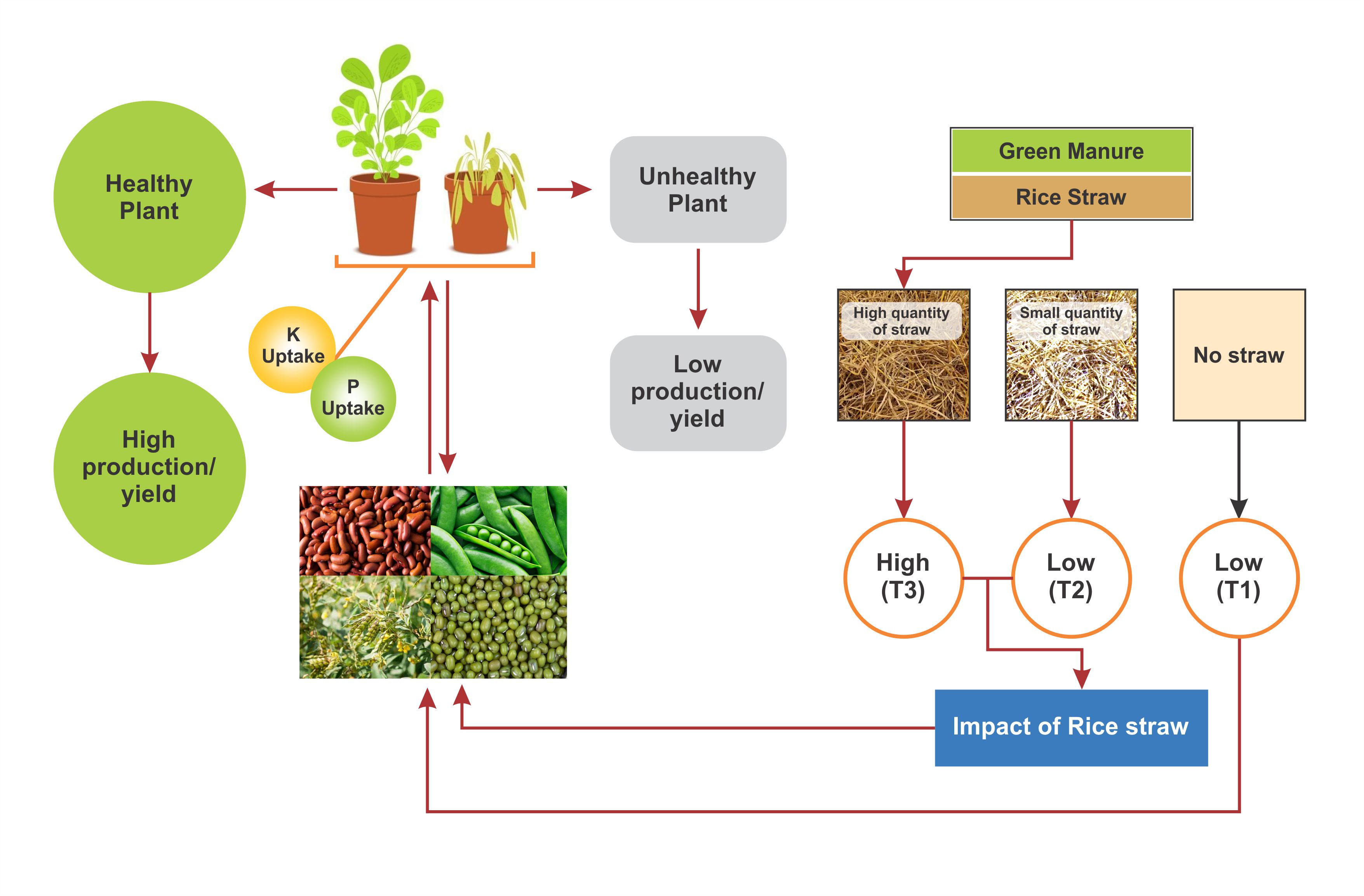
The rice straw incorporation technique is one of the better alternatives for sustainable agro-industry fertilizers. The nutrient uptake capacities of green manure crops during rice straw treatments have not been studied. The pot experiment was conducted from November 2020 to February 2021 at the Sindh province, in the southern region of Pakistan, to investigate the effects of two various rice straw (RS) treatments on different green manure peas (Pisum sativum L.), chickpea (Cicer arietinum L), cowpea (Vigna unguiculata), alfalfa (Medicago sativa), and ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum) varieties biomass yield and amounts of rice straw, such as control (T1): no straw incorporation, (T2): RS incorporation at an amount of 3750 kg ha−1, and (T3): RS incorporation at an amount of 7500 kg ha−1. Compared to the no straw treatment, peas showed the highest dry shoot and root biomass production on the T3 treatment. While the greatest shoot P uptake abilities were recorded in peas at 127.7%, and chickpeas were 51.8% under the T3 straw treatment compared to without straw. Green manure species improved K accumulation capacities under rice straw treatments compared to the control. The plant's shoot and root K uptake capacities showed a significant positive relationship with soil properties, i.e., SOM, TN, NH4+, and AP, respectively. It is concluded that rice straw treatment (particularly in the amount of 7500kg ha−1) is an effective practice for enhancing nutrient uptake capacities in green manure crops and developing soil fertility status.
Total file downloads: 14