- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 52 Downloads
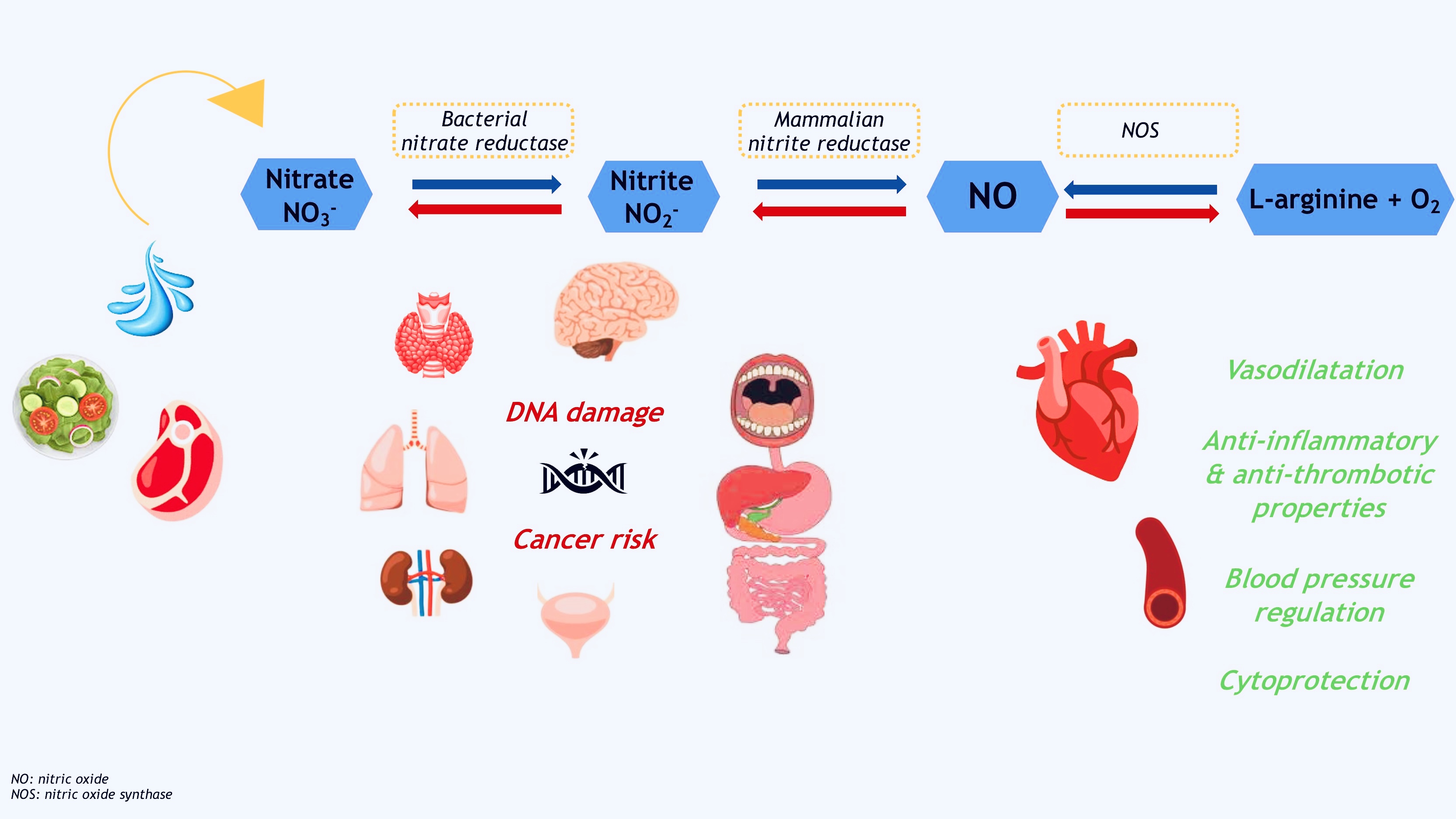
Nitrates are ubiquitous in the environment and key intermediates of various biochemical reactions in the nitrogen cycle, along with nitrites. A considerable source of nitrates is drinking water. There is substantial disagreement among scientists over the current limits for nitrate concentration in drinking water. Most adverse health effects related to drinking water nitrate are likely due to a combination of high nitrate ingestion and factors that increase endogenous nitrosation. The two main health issues are the association between nitrate and (i) cardiovascular diseases and (ii) the incidence of cancer. On one hand, there is evidence for nitrate as a possible cause of serious diseases which remains controversial and on the other hand there is emerging evidence of benefits of nitrate in cardiovascular health. Subgroups within a population may be more susceptible than others to the adverse health effects of nitrate. Here, we discuss the physiologic roles of nitrate and nitrite and their potential effects in order to derive rational bases for dietary recommendations.