- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 56 Downloads
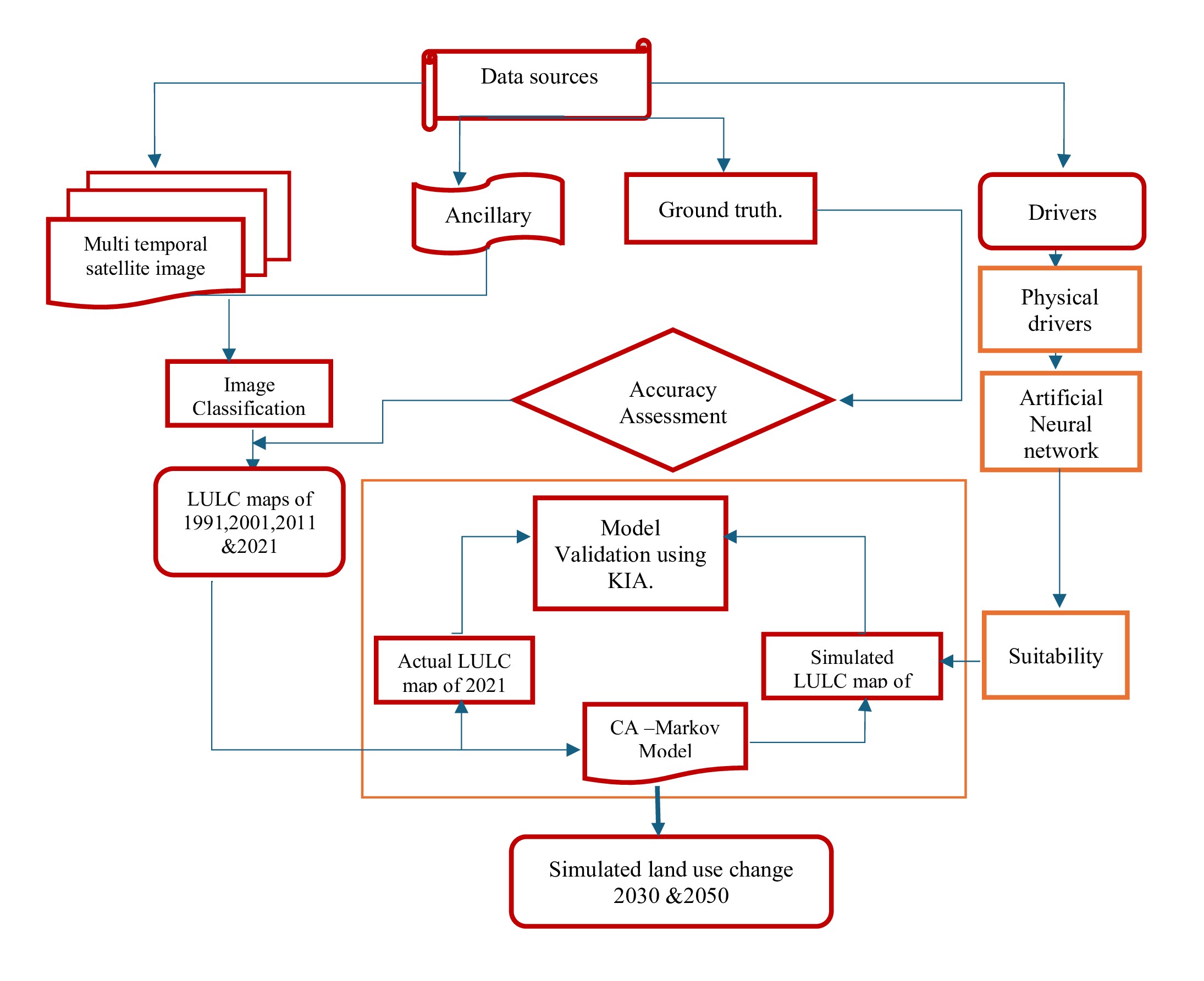
Eco-sensitive Coastal Solar Saltpan (CSS), also known as Saltpan, provides many essential ecological and societal functions. However, changes in coastal saltpan land use resulted in the loss of salt production activities and impacted the socio-economic status of salt workers along the coast of Tamil Nadu. Therefore, it is imperative to ascertain the origins and ramifications of land-use modification within this ecosystem. The change detection results were examined on the parameters of the proportion of land cover classes and change trajectories with particular emphasis on Saltpan. This study used Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models and Cellular Automata - Markov Chain (CA-MC) models to predict the changes in 2030 and 2050. The study shows that the overall Saltpan increased from 1990 to 2021. Results also reveal that saltpan magnitude varies spatial and temporally in coastal taluks. An increasing trend of Saltpan was observed in Vilathikulam, a gradual increase in Ottapidarm, Srivaikuntam &Thiruchendur, and a decreasing trend in Thoothukkudi. The scenario projected for 2030 and 2050 indicated a decline in agriculture and coastal saltpans, while urban land usage increased. Detailed predictive models of the saltpan dynamics base on coastal land-use change can be highly advantageous in developing management strategies for sustainable coastal ecosystems.