- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 32 Downloads
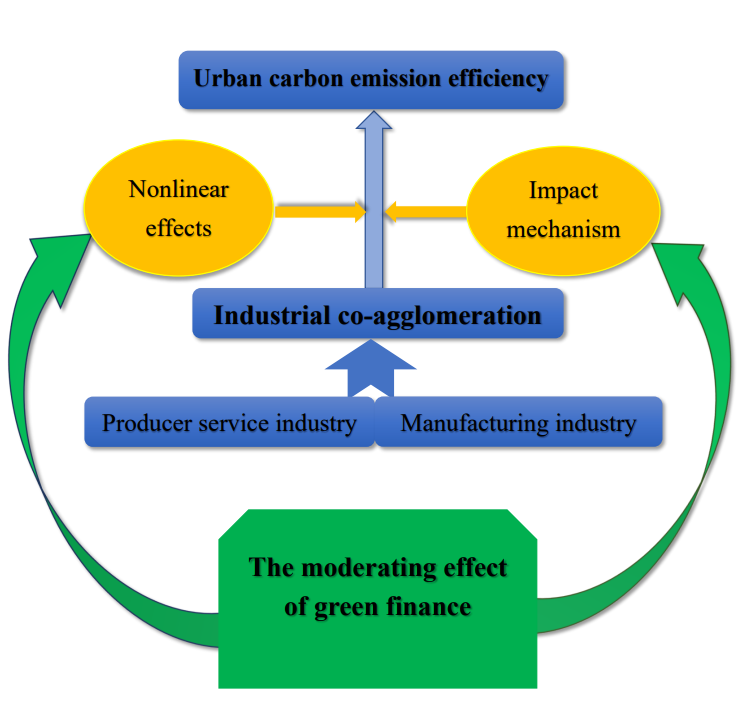
This study explores the impact of line-height:200%;font-family:"Times New Roman",serif">industrial co-agglomeration on urban carbon emission efficiency in Shandong Province from China during 2007 to 2020. The moderating effect model is constructed to explore the role green finance in the impact of industrial co-agglomeration on urban carbon emission efficiency. We explore the influence mechanism of industrial co-agglomeration on urban carbon emission efficiency. Through conditional process analysis, we investigate the moderating effect of green finance in the mechanism of industrial co-agglomeration on urban carbon emission efficiency. Empirical results indicate that: (1) The impact of industrial co-agglomeration on urban carbon emission efficiency is inverted U-shaped. (2) Green finance has a positive moderating effect in the impact of industrial co-agglomeration on urban carbon emission efficiency. (3) Industrial co-agglomeration affects urban carbon emission efficiency through scale effect, technological effect and structural effect. (4) Green finance plays a moderating role in the impact pathways of industrial co-agglomeration on urban carbon emission efficiency. Therefore, this paper proposes targeted recommendations to improve urban carbon emission efficiency according to industrial co-agglomeration and green finance development.