- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 18 Downloads
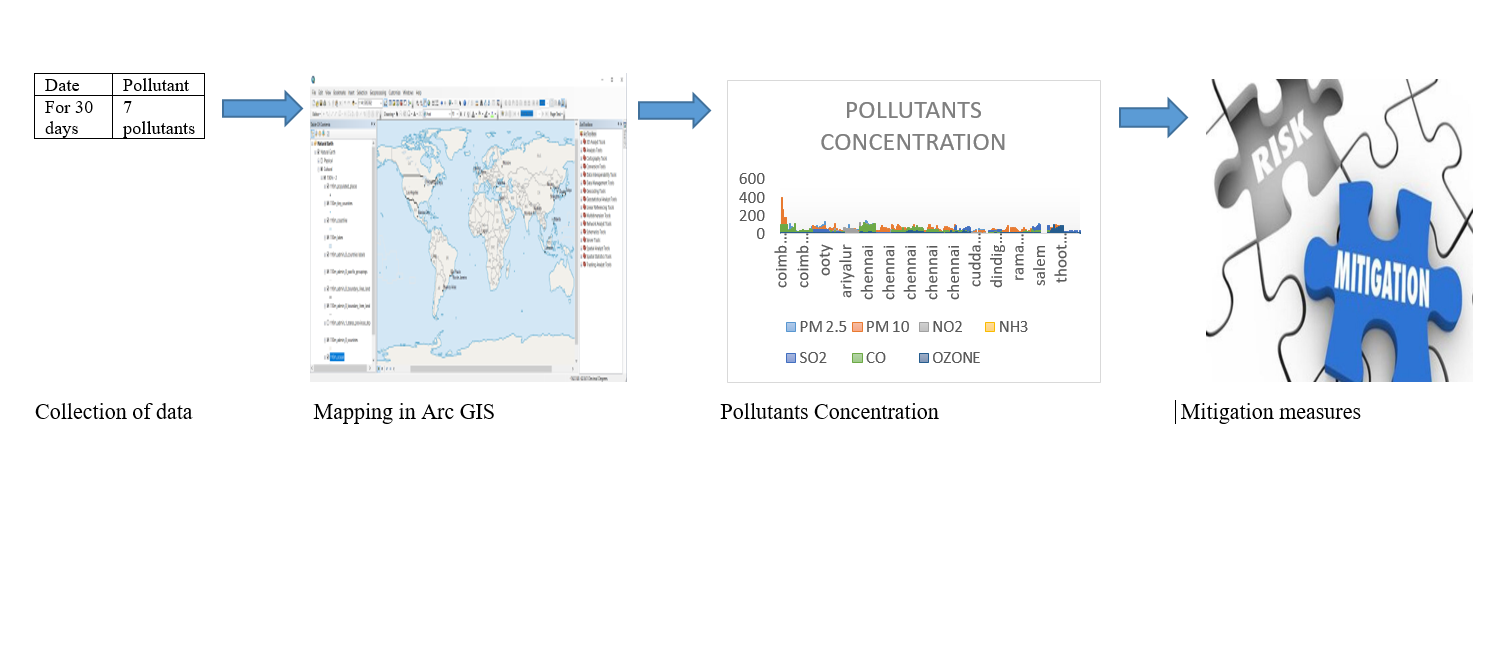
Air pollution in Tamil Nadu has become a pressing issue, as various pollutants have surpassed the limits established by the pollution control board. The major air pollutants in the region, namely sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and suspended particulate matter, have been identified. This study aims to monitor and analyse the levels of air pollution in Tamil Nadu, with a specific focus on key parameters such as SO2, NO2, PM2.5, PM10, and ozone. By examining the atmospheric levels of these pollutants and their correlation with temperature fluctuations, the impact on human health and respiratory problems can be evaluated. Moreover, the study will assess the contribution of traffic emissions and vehicular pollution to the concentration of PM10 in different areas. Additionally, GIS technology will be utilized to spatially and temporally investigate pollution concentrations and evaluate their effect on the air quality index. By comparing the pollution concentration from thermal power stations and vehicular pollution, the study will identify the sources of pollutants, with a particular emphasis on SO2 and NOx emissions from vehicles and higher levels of suspended particulate matter from thermal stations. The analysis of these pollutants and their sources will provide valuable insights for the implementation of effective pollution control measures and the management of environmental pollution in Tamil Nadu. Given the concerns regarding pollutants exceeding the prescribed limits set by the pollution control board, monitoring air pollution in Tamil Nadu is of utmost importance.