- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 8 Downloads
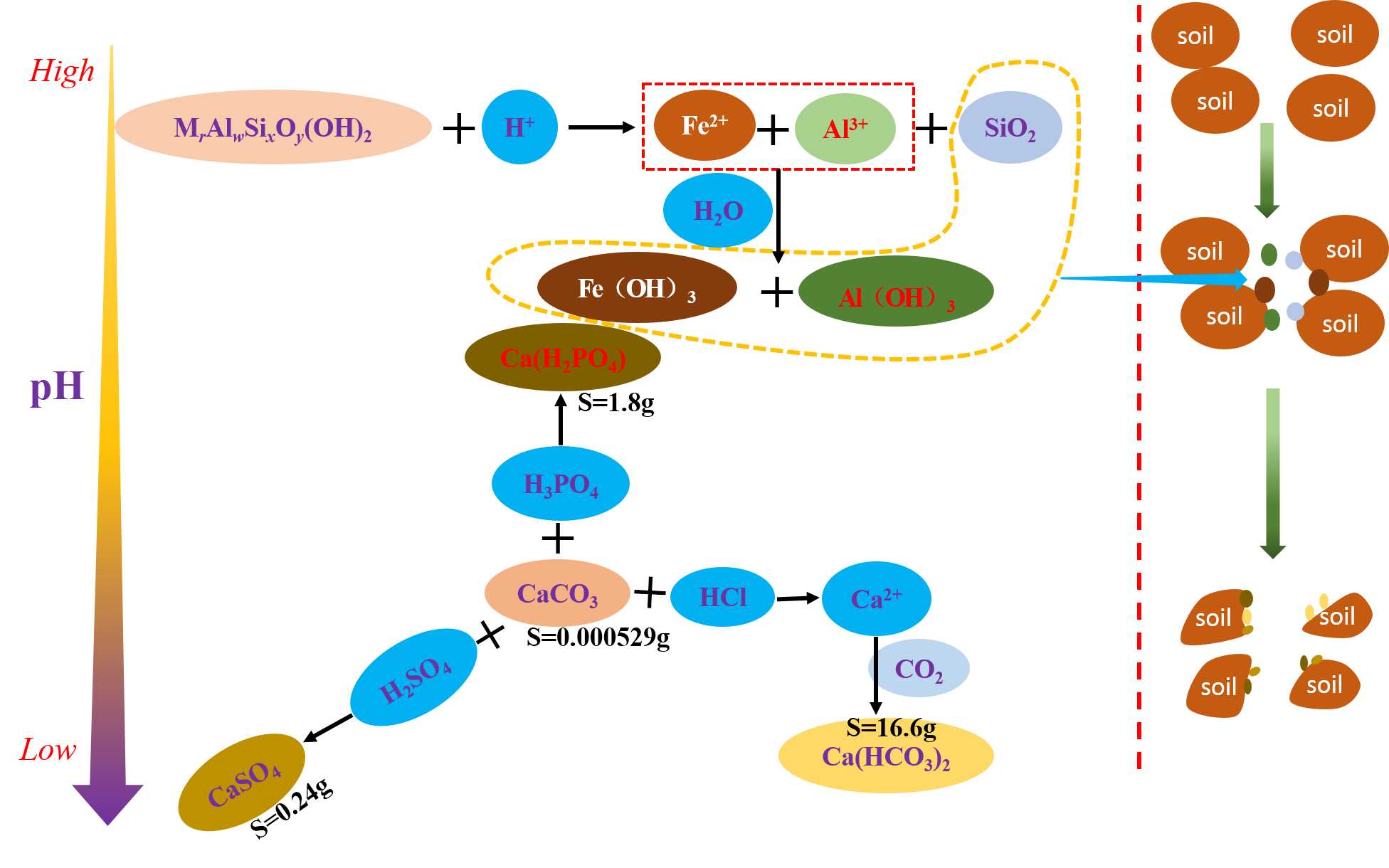
Most of the tungsten tailings (TTs) are filled in the open. As a result, the phenomenon that acid rain influences the engineering geological characteristics of tungsten tailings is impossible to avoid, especially in southern China, where acid rain occurs frequently. This work studied the permeability properties of TTs treated with different acid solutions. The HCl, H2SO4, and H3PO4 solutions were prepared as the permeate fluids with pH values of 7, 5, 4, and 3. The falling head permeability test studied the TTs’ permeability characteristics under different acid solutions action. The microscopic mechanism of the movement of the acid solutions and TTs was analyzed based on X-ray diffraction results and nuclear magnetic resonance. The experimental results show that the permeability coefficient of TTs decreases first and then increases with the pH value of HCl and H2SO4 solutions and first increases and then decreases and then increases with the pH value of H3PO4 solutions. When the pH value >3, the effect of acid on the permeability coefficient is satisfied with HCl >H2SO4> H3PO4; otherwise, it is satisfied with H2SO4> H3PO4> HCl. The development law of T2 spectrum distribution is consistent with the permeability coefficient of TTs treated with the same acid solution. The acid solutions react with chlorite and calcite in the tailings, which affects the permeability of TTs treated by the acid solution. Therefore, preventing the infiltration of acid solutions from entering the tailings is conducive to improving the stability of tungsten tailings dams.