- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 11 Downloads
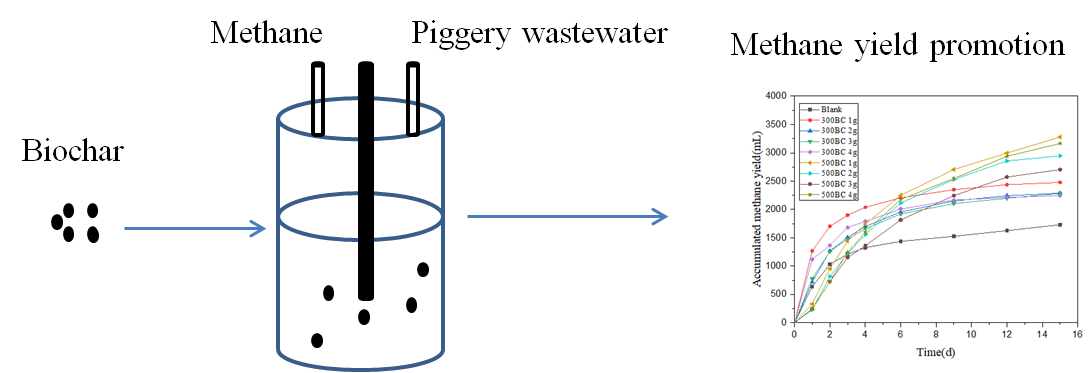
Anaerobic digestion of piggery wastewater mediated with biochar was investigated by COD removal rate, methane yield, process stability and microbial community analysis. The results showed that biochar could effectively improve the COD removal rate and methane yield. Compared with blank group, COD removal rate was increased by 2.3%-9.4% for 300BC and by 37.5%-44.0% for 500BC. The maximum methane yield was obtained in 1g 300BC and 500BC, which was increased by 43.20% and 89.52% respectively. Meanwhile, the final H2S concentration was also obviously decreased by BC. Microbial community analysis showed that the addition of BC could increase the abundance of methanogens compared with the blank group. 500BC had a higher positive effect on anaerobic digestion of methanogenic bacteria than 300BC.Meanwhile, the relative abundances of hydrotrophic methanogens in 500BC groups were significantly higher than that of acetoclastic methanogens in 300BC.