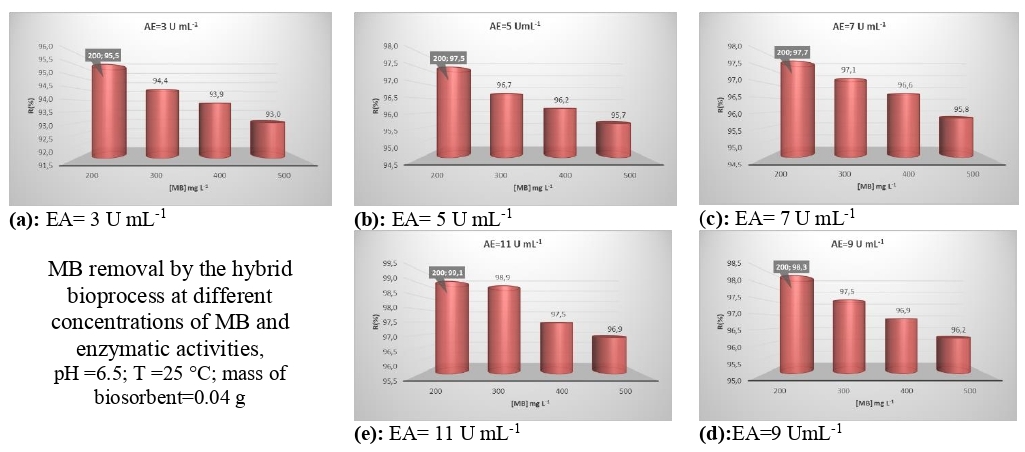
Methylene blue (MB) removal from aqueous media using hybrid bioprocess: biosorption on modified cork powder (SDS-cork) and soluble turnip peroxidase (STP) was investigated. Cork powder was modified with sodium lauryl sulphate (SDS). Chemical composition of the biosorbent were characterized by infrared before and after biosorption. The hybridization was carried out under the optimal conditions of the two processes: pH=7, T=40 °C, [H2O2]=10 mM for enzyme activity(EA)=7 U mL-1 witch it was in excess for the EA= 5 and 3 U mL-1, [H2O2] = 15 mM for EA= 9 U mL-1 and [H2O2]=15 mM for EA= 11 U mL-1 with a treatment time that equals the sum of two optimal treatment times, and a mass of SDS-cork 0.04 g with a diameter <0.16 mm. The feasibility and performance of this hybridization was tested according to two parameters the initial concentration of MB which varied between 200 and 500 mg L-1 and the enzymes activities which has varied between 3 and 11 U mL-1. The minimum removal percentage of MB was satisfactory according to 93% for [MB] = 500 mg/L and an EA of 3 U mL-1, otherwise the maximum removal percentage was very satisfactory being in the order of 99.9% for a [MB] = 200 mg L-1 and EA= 11 U mL-1.
Total file downloads: 3