- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 26 Downloads
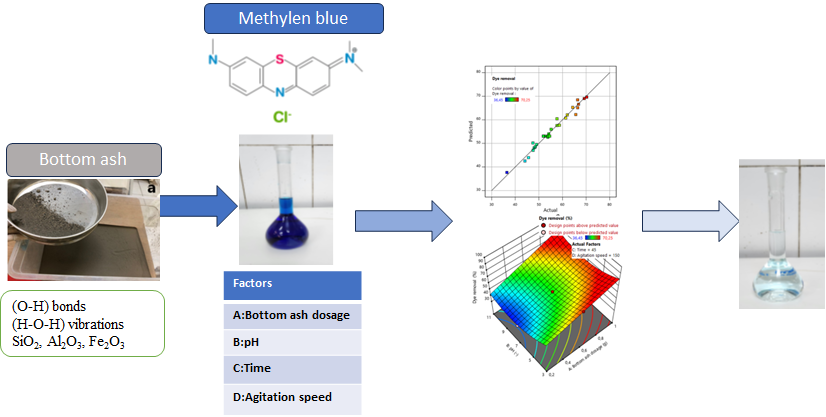
This study investigated the removal of methylene blue (MB) via adsorption using waste bottom ash. The bottom ash, sourced from a waste storage site in the Çorlu district of Tekirdağ province, Thrace Region, was utilized as the adsorbent. The research examined the impact of several variables on MB removal, including bottom ash dosage, pH, contact time, and agitation speed. It was found that all parameters had a single-variable effect, while pH exhibited a quadratic effect on MB removal in a model-based analysis. The optimization of the model for maximum MB removal identified the optimal conditions as 0.978 g bottom ash dosage, pH 3, 15 minutes of adsorption time, and 50 rpm agitation speed. Under these conditions, the model predicted an MB removal efficiency of 71%, which was experimentally confirmed to be 72.5%. The adsorption process was found to fit with the Freundlich isotherm, indicating a multilayer adsorption mechanism on the heterogeneous surface of the adsorbent. This research not only highlights the feasibility of using bottom ash from coal combustion as an economical adsorbent for dye-contaminated wastewater but also underscores its potential to inform and inspire future studies on waste recycling and wastewater treatment.