- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 7 Downloads
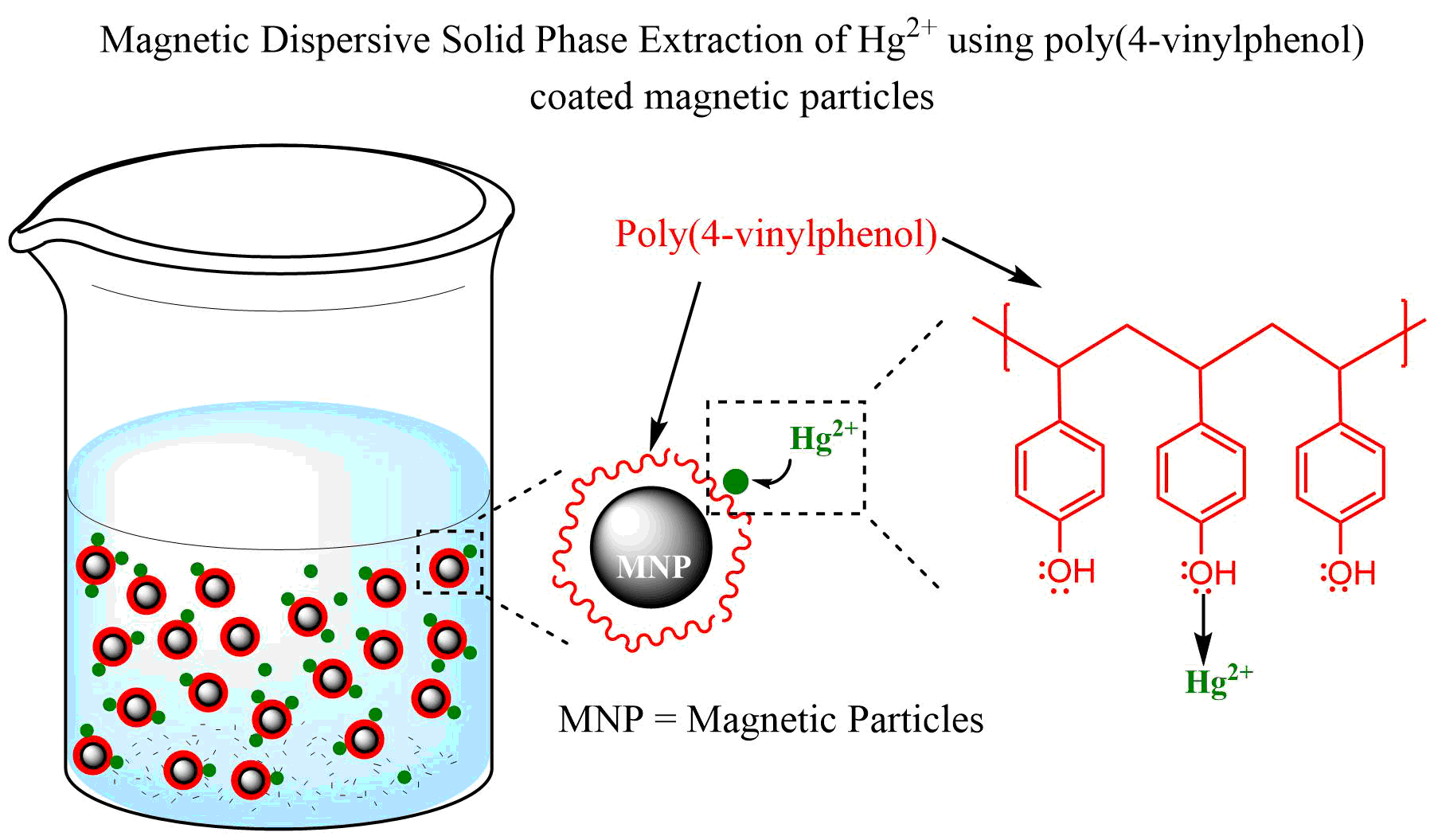
The development of magnetic sorbent for dispersive solid-phase micro-extraction (DmSPE) often requires lengthy multi-step reactions. This research revealed a simplified method for preparing magnetic sorbent for the DmSPE using poly(4-vinylphenol) (PVP). The magnetic sorbent (PVP@MNP) was prepared by coating PVP on magnetic particles (MNP). The characterization and formation of PVP@MNP were confirmed using infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscope, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The primary goal of this study is to develop a sensitive DmSPE method to analyze Hg2+ in water using PVP@MNP as a magnetic sorbent. The preparation of PVP@MNP was performed in a simple coating method at room temperature. Briefly, the PVP@MNP was prepared by sonicating the mixture of MNP and PVP. This sorbent was then used as a magnetic sorbent for the extraction of Hg2+ from water. The developed PVP@MNP based DmSPE reached a low method of detection limit (0.01 μg L-1) and limit of quantification (0.04 μg L-1). This method also showed a wide linearity range (100 - 2000 µg L-1) with a good correlation factor under optimized conditions. The developed method showed good recovery (72-90%) with good intraday and interday precision. This study also showed that the developed DmSPE method was effectively used to determine Hg2+ in drinking water, mineral water, and surface water. The result also demonstrated that PVP@MNP is reusable.