- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 11 Downloads
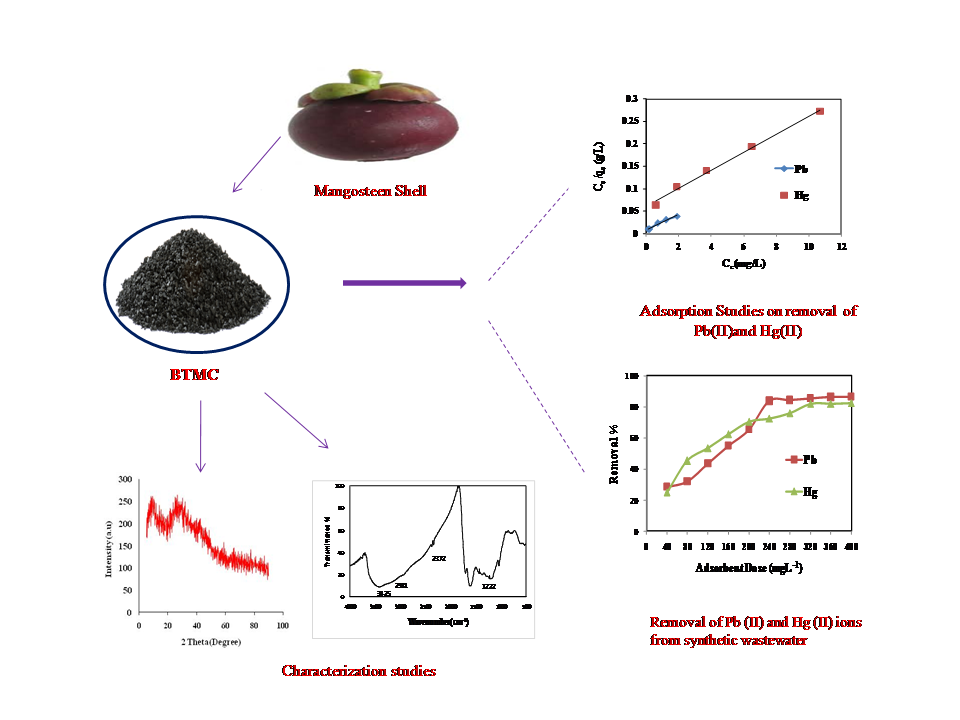
An adsorbent was prepared from Mangosteen shell using sulphuric acid and sodium bicarbonate as modifiers. Bicarbonate treated mangosteen shell (BTMC) was characterized using FT- IR, SEM, EDAX and XRD data. The Freundlich adsorption isotherm model gives a good fit. The maximum adsorption capacities of BTMC were found to be 58.48 mg g-1 and 49.75 mg g-1 for Pb (II) and. Hg (II). Adsorption of Pb (II) and Hg (II) followed pseudo-second-order kinetics. The adsorption mechanism was explained using the Weber and Morris's intra-particular diffusion process. Batch mode studies with synthetic wastewater suggest that BTMC can be efficiently used in wastewater treatment.