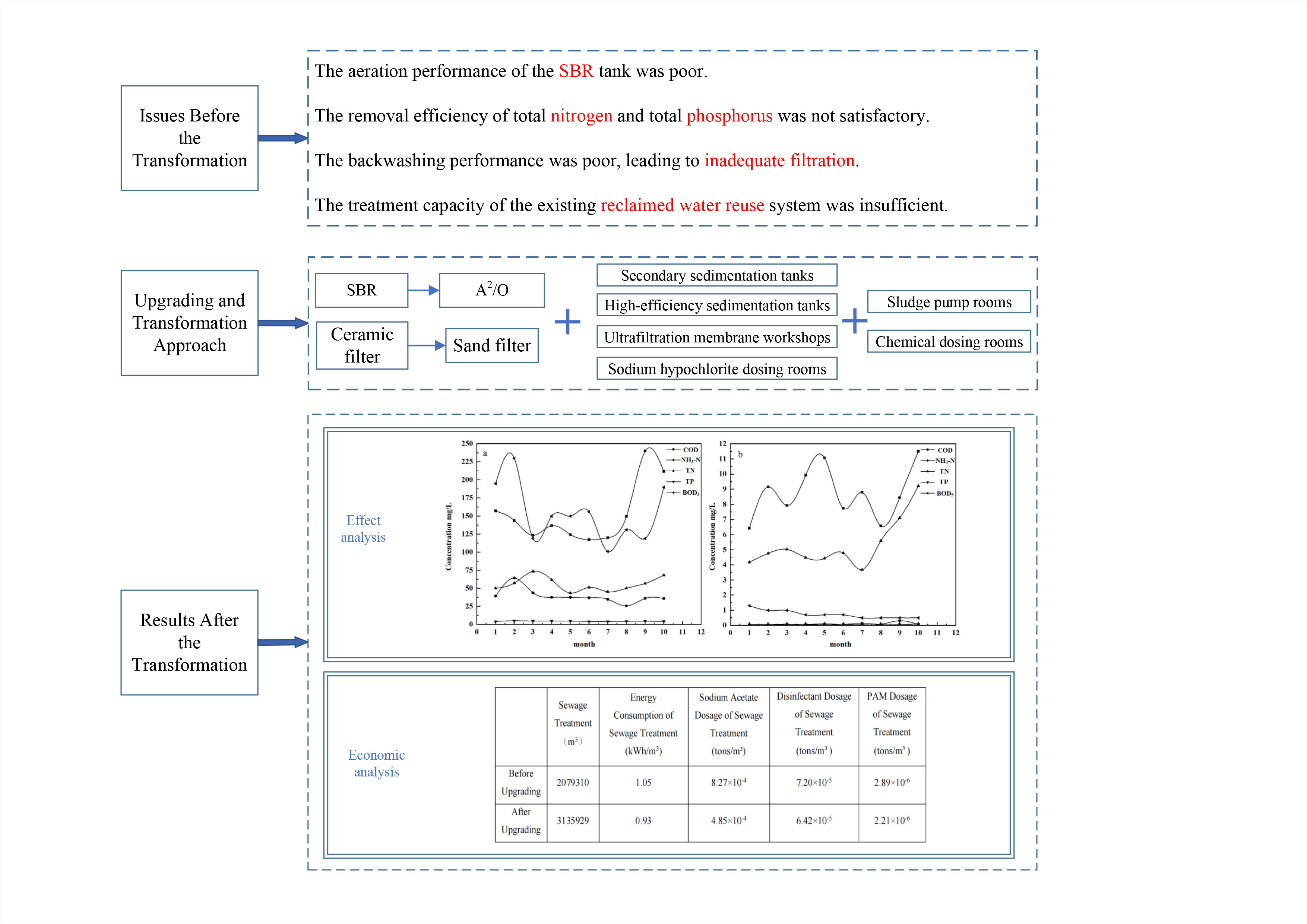
The effluent quality of a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) in Hebei Province met the Class I-A standard of "Discharge Standard of Pollutants for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants"(GB 18918-2002) (COD≤50 mg/L, TN≤15 mg/L, TP≤0.5 mg/L, NH3-N≤8 mg/L). However, under the guidance of energy conservation and emission reduction, existing WWTP were faced with some limitations, such as ineffective phosphorus and nitrogen removal, and upgrading treatment standards were required. Existing facilities are fully used and the synergistic strategy of enhancing biological efficiency and deepening treatment processes are adopted to achieve reduction of pollutants such as organics, nitrogen and phosphorus. The results show that the removal rates of COD, NH3-N, TP and TN reaches 94.6%, 99.8%, 86.5% and 98.0% respectively, even with the influent flow having increased by 50.8%, enabling the effluent to meet strict discharge standards (Class B standard of Beijing's "Comprehensive Discharge Standard for Water Pollutants") (DB11/307-2013) (COD≤40 mg/L, TN≤15 mg/L, TP≤0.4 mg/L, NH3-N≤5mg/L). The electricity consumption decreases by 11.4%, and the usage amounts of sodium acetate, disinfectant, and polyacrylamide respectively decrease by 41.4%, 10.8%, and 23.5%. This project significantly improves the local environment and protects downstream ecosystems. It provides valuable reference insights for similar WWTPs.
Total file downloads: 9