- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 12 Downloads
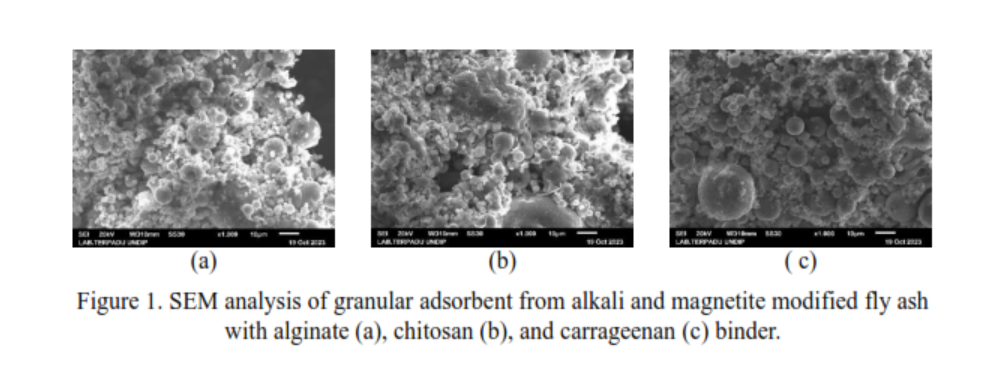
The presence of dye pollutants in the aquatic environment, apart from causing aesthetic problems, can also cause health problems. Removal of dye pollutants in industrial wastewater can be done using the adsorption method, which is a simple, effective and low-cost process. Fly ash is a solid waste from the coal combustion process which has been widely used as an adsorbent in wastewater treatment containing dyes. In this research, fly ash was used as an adsorbent for naphthol AS dye through modification with alkali and magnetite, and granulation with a binder so that it would facilitate its application on a large scale. The influence of the type of binder (alginate, chitosan, carrageenan) and adsorption variables (pH, contact time, initial concentration of dye) have been studied in this research in addition to studying the adsorption kinetics and isotherms. Granulation of alkali and magnetite modified fly ash was best obtained with carrageenan binder compared to alginate and chitosan binders. Granular alkali and magnetite modified fly ash with carrageenan binder have the best adsorption ability of naphthol AS dye at pH 3, initial concentration of 50 mg/L, and contact time of 120 minutes and follow the pseudo-second-order adsorption kinetics model and the Freundlich adsorption isotherm model.