- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 20 Downloads
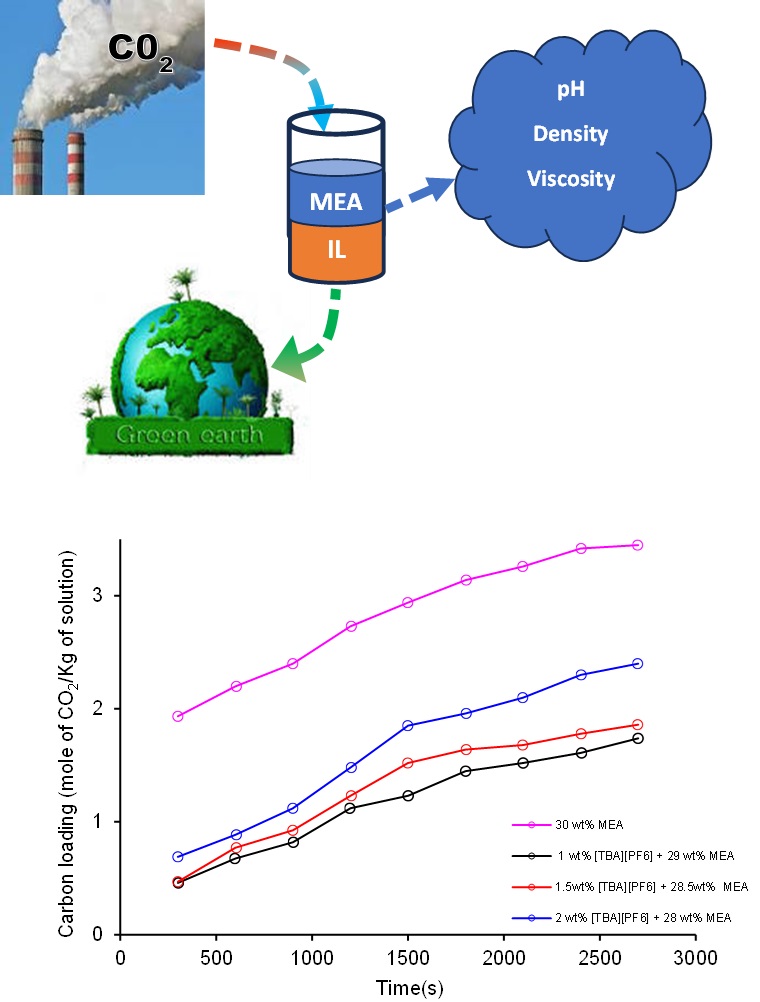
Climate change is a prime threat to human health and the environment. Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions play a pivotal role in global warming, the greenhouse gas effect, destroys the ecosystem. This impact of climate change can be prevented with the help of a solvent-based CO2 absorption process. In this study, amine-ionic Liquids (IL) were used as a solvent blend for the CO2 absorption process. The non-aqueous solvent blend Monoethanolamine (MEA) - Ionic Liquid (IL) namely tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate [TBA][PF6] and their total concentration was kept at 30 wt% throughout the study. The thermophysical properties such as density, dynamic viscosity, surface tension, pH and carbon loading of virgin and carbon-loaded non-aqueous amine-IL have been measured before and after the absorption process experimentally. This study was extensively carried out for varying temperatures (293.15 to 333.2 K) and IL concentration (1-2 wt%) at intervals of 10 K and 0.5 wt% respectively. All the measured thermophysical properties of amine-IL show a significant increase in the IL concentration. Conversely, it declines while increasing temperature. Higher carbon loading was observed for 2wt% IL+28wt% MEA, compared to 30wt% MEA, even though increased viscosity was obtained at this composition. This non-aqueous amine-IL solvent might favor sustainable development in CO2 capture process.