- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 22 Downloads
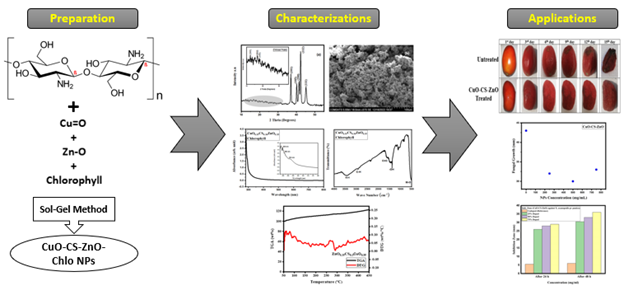
Chitosan-doped copper oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles (CuO-CS-ZnO NPs) were prepared utilizing sol-gel synthesis route. Chlorophyll was added in the process of making NPs to enhance the effects of these NPs. The prepared NPs were thoroughly analyzed using advanced techniques including X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV-Visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy, Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Structural analysis revealed the successful synthesis of irregular shaped NPs with average crystallite size of 10.7 nm. In optical properties, UV-Vis showed the absorption bands associated with different absorption centers in the sample and FTIR revealed various function groups associated with the preparation procedure and chemical used while synthesizing these NPs. On applications side, these NPs efficiently resist the growth of X. axanopodis pv punicea bacteria within 24-48 hours of investigation. Same NPs showed effective antifungal effects on the Alternaria solani. Finally, these NPs were used as food preservative agents where tomatoes were used as the target fruit. Tomatoes coated with NPs exhibited better preservation and a longer shelf life.