- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 8 Downloads
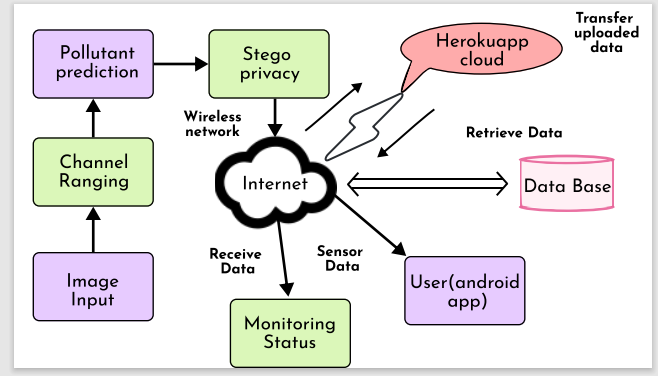
Monitoring air quality in polluted environments is crucial for human health, but traditional methods using meteorological equipment have limitations in complex terrains and are costly. This study proposes a novel approach to address air pollution monitoring in urban areas by visually assessing the haziness of distant photos. We explore the correlation between air quality indexes (e.g., AQI, PM2.5, PM10) and haziness levels in monitoring images. Results indicate that objective indicators accurately reflect air pollution levels, regardless of image size. To implement this observation practically, we introduce a new method called the "Channel ranging based prediction model in cloud with steganography-based privacy preservation framework." This model calculates a ratio between dark and bright channel information in scaled images, serving as a visual index of air pollution. Experimental findings demonstrate the effectiveness of this metric in terms of correlation, computational speed, and classification accuracy compared to existing metrics.