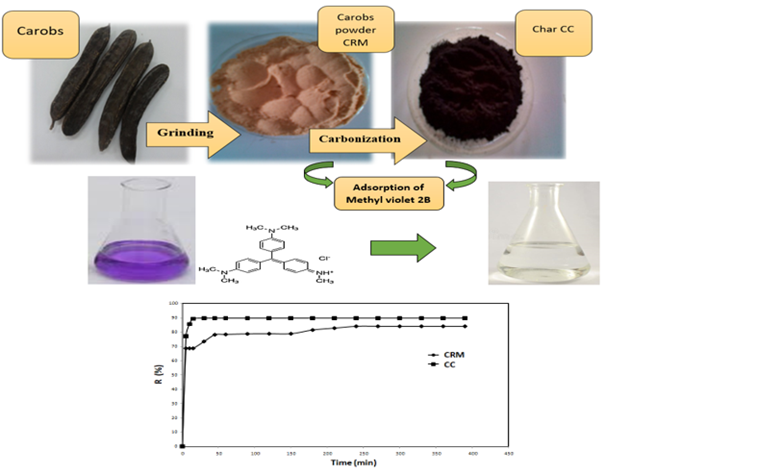
In the present study, fruits of Ceratonia siliqua L. (carobs) were used as an alternative low cost biosorbents to remove a cationic dye, methyl violet 2B (MV) which has broad applications in paints, textile and printing ink, from aqueous solutions. The untreated (CRM) and thermal treated carobs (CC) were characterized by BET, FTIR, XRD and SEM techniques. The influences on MV adsorption of various experimental factors such as particle sizes, contact time, stirring speed, adsorbent dose, solution pH, temperature, ionic strength and initial MV concentration were investigated. Adsorption kinetics was found to be best represented by the pseudo second order model. The isotherm analysis indicated that the adsorption data could be represented by the Langmuir model for CRM and CC at 20°C. The maximum adsorption capacity for MV was 62.5 mg/g onto CC and 9.804 mg/g onto CRM. Thermodynamic parameters showed that the process was spontaneous and exothermic.
Total file downloads: 11