- gnest_04158_published.pdf
-
Paper IDgnest_04158
-
Paper statusPublished
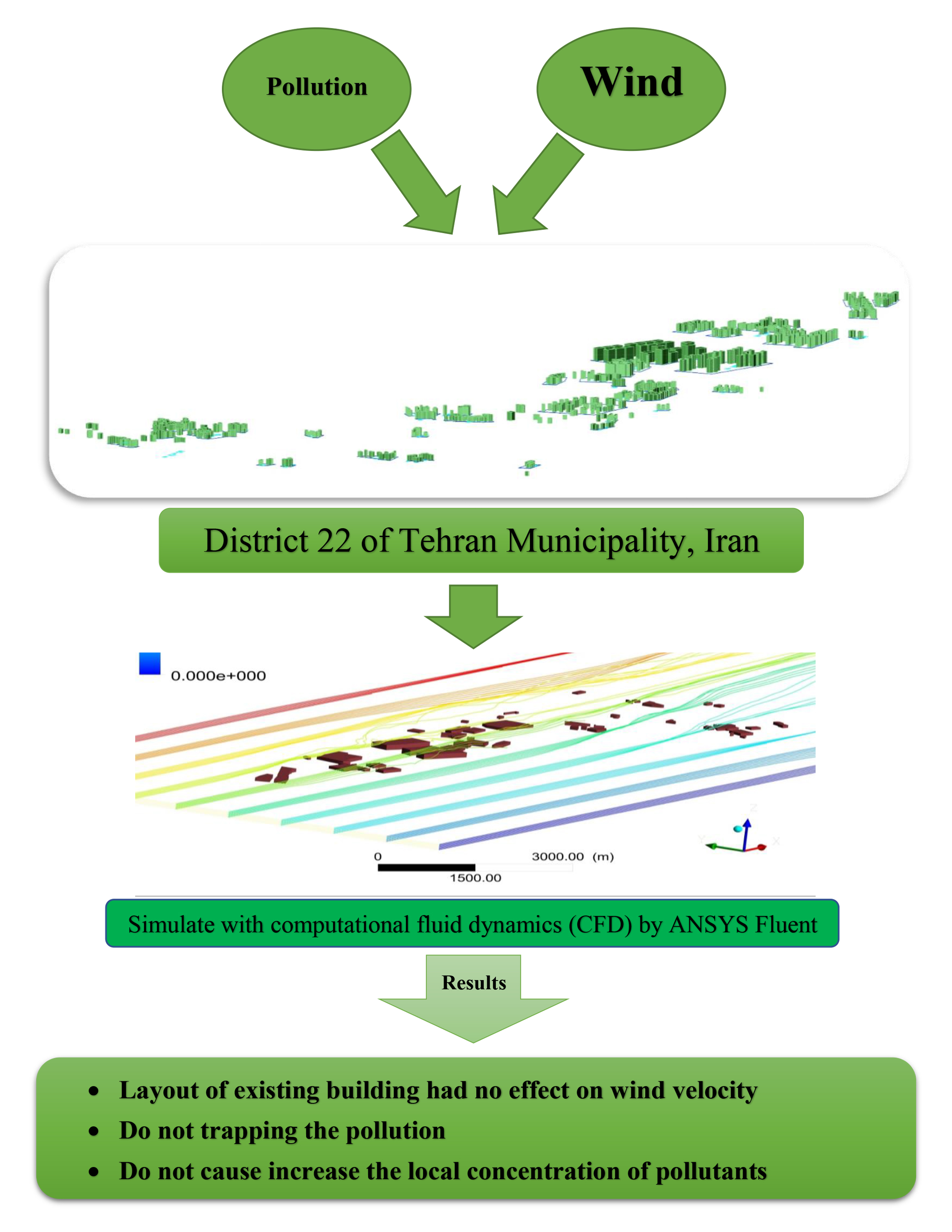
The large cities are facing with a phenomenon called high-rise buildings which is due to the increasing of the population and also developing the cities. One of the negative impacts of high-rise buildings is the change in urban wind flow. Air pollutions is a major problem in the cities and the wind play an important role in the dispersion of air pollutions. The most probable wind direction for Tehran is west and hence district twenty-two of Tehran municipality which is located in northwest of Tehran (Capital of Iran) is in the dominant direction of wind flow. This paper presents a numerical method to investigate the interaction between the wind flow, pollution and high-rise buildings in district twenty-two of Tehran municipality. The effect of these phenomenon on the other regions is considered as well. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) by ANSYS Fluent software has been used in order to simulate the problem. The results of this study indicate the existing buildings and their layout had no effect on wind velocity and trapping the pollution and do not cause an increasing of the local concentration of pollutants. So the geometry and layout of buildings allow the flows and environmental pollutants to pass.
Total file downloads: 1