- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 5 Downloads
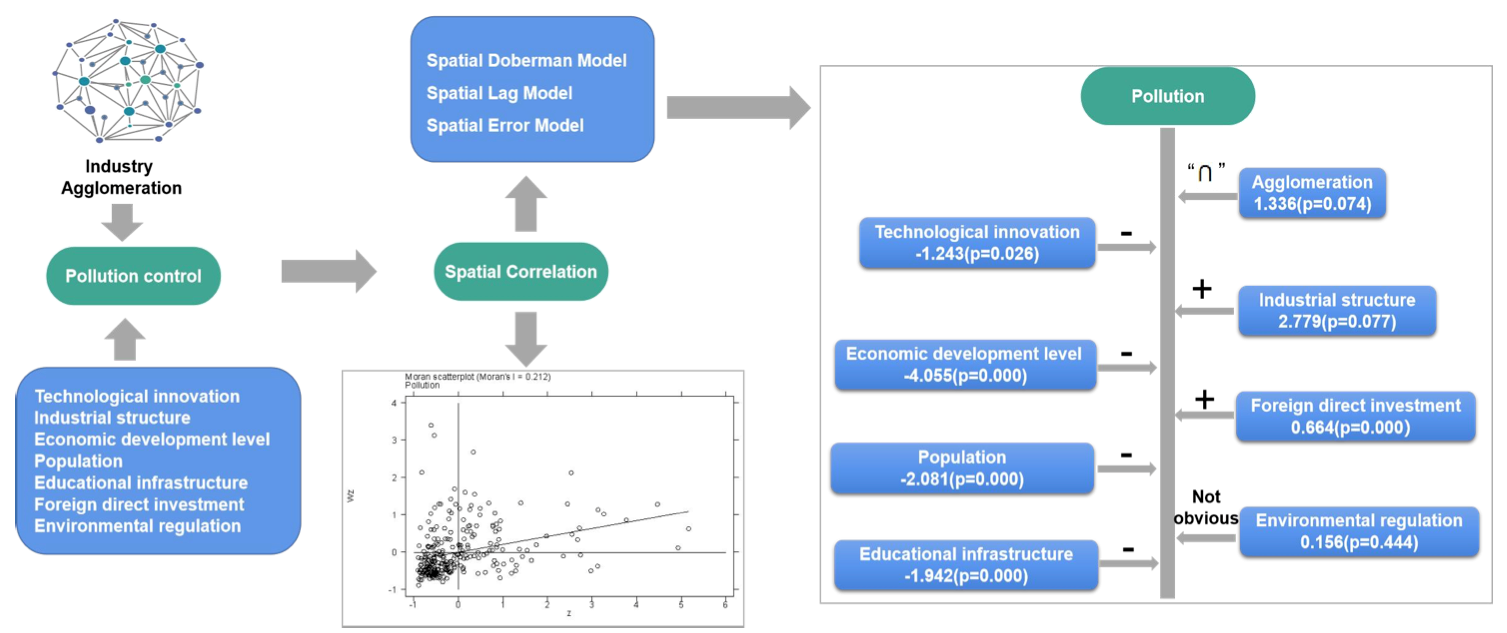
To find out the relationship between industrial agglomeration and environmental pollution, this paper carried out empirical research on the panel data collected from 271 prefecture-level cities in China from 2004 to 2017 through a spatial panel econometric model. It reviewed the influence of agglomeration externality on environmental pollution. The results detected an inverted "U"-shaped relationship between manufacturing industry agglomeration and environmental pollution nation-wide. The manufacturing industry agglomeration level at the inflection point was 0.652, suggesting that prefecture-level cities suffered severe environmental pollution problems. At the regional level, the manufacturing industry agglomeration in eastern and western China had a significant adverse effect on environmental pollution. In the central China, the relationship between manufacturing industry agglomeration and pollution was "N" -shaped. The manufacturing industry agglomeration levels in most prefecture-level cities were between the two inflection points. The environmental pollution aggravated as the manufacturing industry agglomeration level rose in the range. As for cities in the northeastern region, manufacturing industry agglomeration has no direct causal relationship with environmental pollution.