- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 5 Downloads
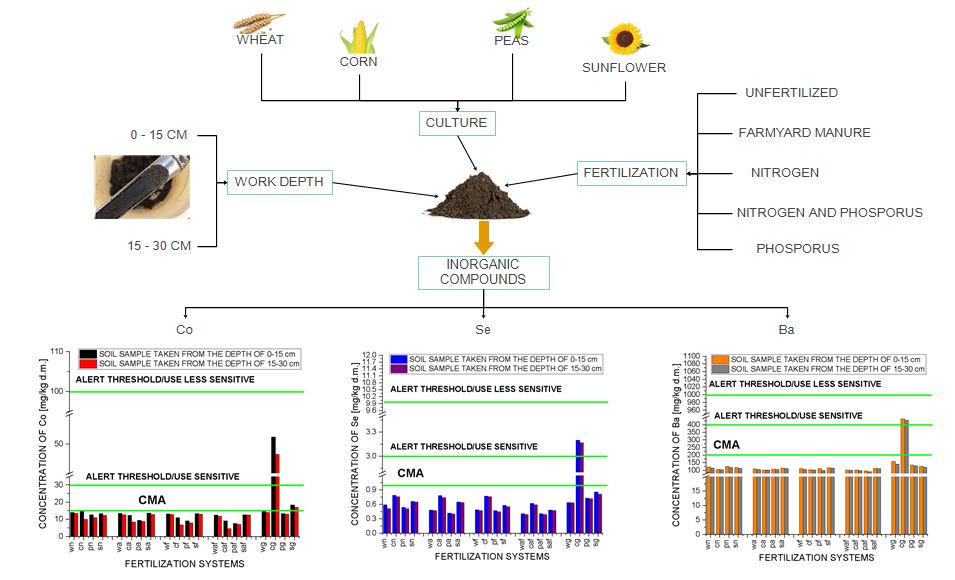
The main objective of this article is to observe the variation of the content of inorganic compounds in the soil (cobalt, selenium, barium) under the influence of fertilization systems applied to different monocultures of cereals (wheat, corn), leguminous (peas) and oleaginous (sunflower). High concentrations of cobalt, selenium and barium with phytotoxicity effect on the soil and future crops were recorded mainly in the experimental parcels cultivated with corn, respectively with sunflower and fertilized with farmyard manure. The highest phytotoxicity effect on soil and future crop was recorded in the case of cobalt, for the experimental monoculture variant of corn fertilized with farmyard manure where the cobalt concentration in the soil exceeded the alert threshold / sensitive use (AT/SU) for inorganic compounds in the soil (51.2 mg/kg d.m.).