- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 20 Downloads
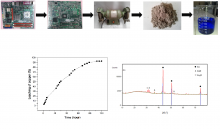
In this research, the selective leaching of copper from waste printed circuit boards (PCBs) using glycine as a complexing agent was investigated. PCBs were pulverized and sieved, which allowed obtaining a PCBs powder of particle size fraction ≤ 1mm. The PCBs powder has been characterized by several techniques before and after leaching. In order to understand the copper extraction process, the reaction mechanisms, and to determine the optimal leaching parameters, the effects of a range of parameters during copper leaching were investigated, including leaching time, solid-to-liquid ratio, mechanical stirring rate, leaching temperature and glycine concentration. Copper leaching from PCBs waste powder was identified as a complex four-stage gas-liquid-solid process that is carried out slowly under ambient conditions. Glycine shows a very significant selectivity for copper during leaching process allowing dissolving copper from PCBs waste with a percentage of 92.8% under ambient conditions.