- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 2 Downloads
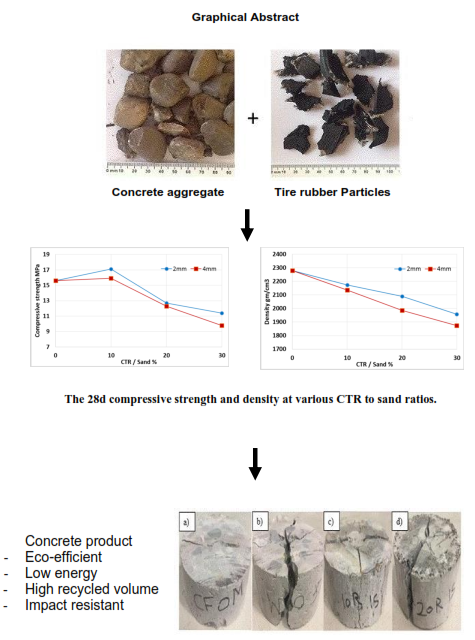
One of the major challenges faced by researchers is to recycle industrial wastes in a manner that reduces their environmental impact in nature. An experimental study was carried out to determine the suitability of using chopped tire rubber as reinforcements in green and sustainable geopolymer concrete, with the purpose of using them as nonstructural products. The geopolymer mixture was made by mixing of fly ash powder, fine aggregate, and Superplasticizer in Na2SiO3/NaOH solution. Mixtures were divided into four different groups, with constant water to fly ash ratio of 0.12 and alkaline dosage of 45% by weight of fly ash, based on the recycled chopped tire rubber (CTR) content: 0, 10, 20, and 30% by volume of fine aggregate with two maximum sizes (2 and 4mm). Hardened properties of resulted geopolymer like compressive strength, density; and ultrasonic pulse velocity were examined at 28d. Besides that, X-Ray diffractometer and Scanning Electron Microscope were used in order to observe the microstructure of the resulted geopolymer concrete. In view of the consequences for this study, it is preferable to replace no more than 10% of fine aggregate in geopolymer concrete by CTR. In addition, according to SEM photographs, increasing the CTR content more voids will be pronounced and thus, decreasing the mechanical performance.