-
VolumeVolume 22 (2020)
-
Issue
-
Pages315-319
- gnest_03088_published.pdf
-
Paper IDgnest_03088
-
Paper statusPublished
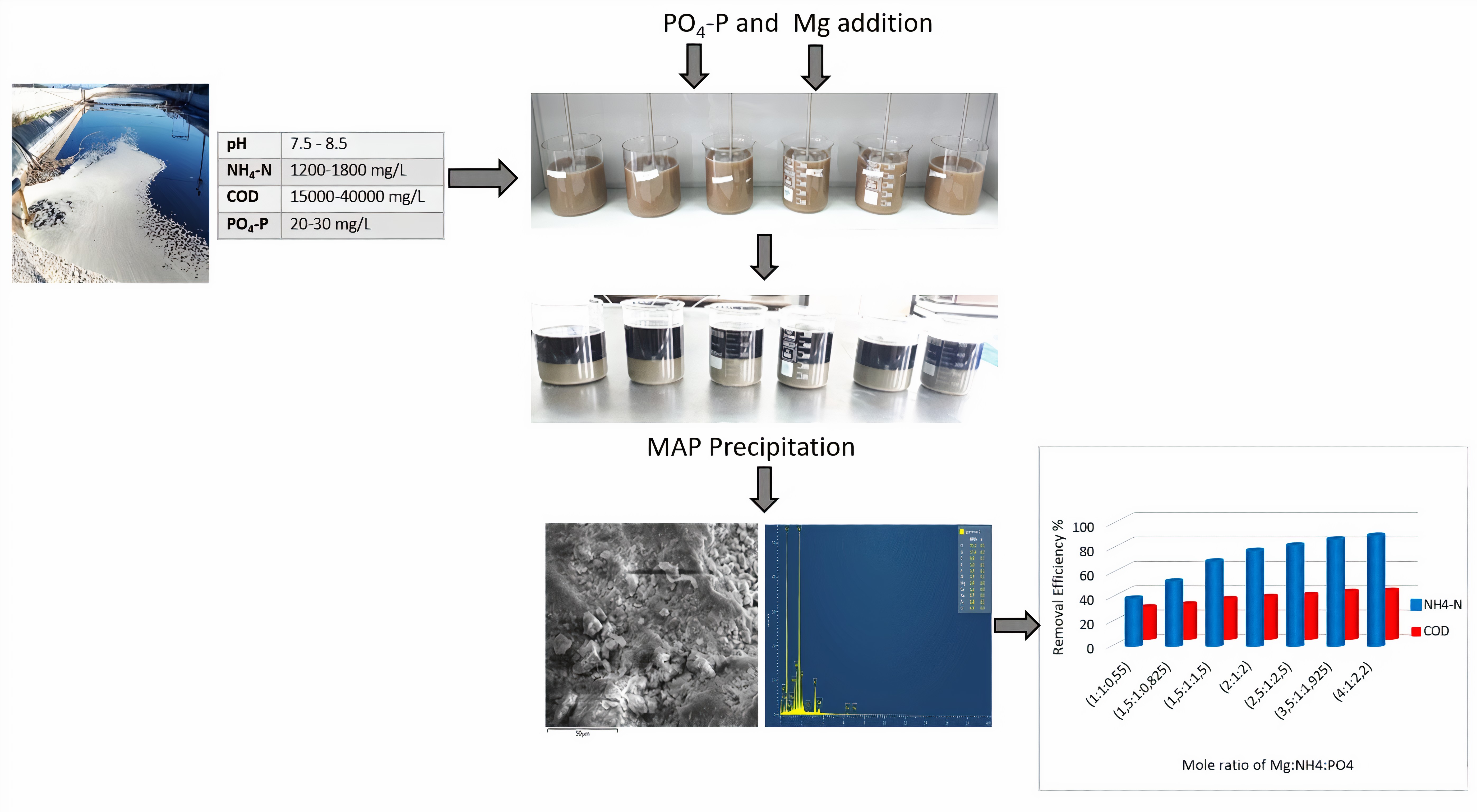
Most of the major cities in our country are opposed to the problem of water pollution due to the uncontrolled leachate resulting from the decomposition of solid wastes in irregular landfills. The waste waters that have high nitrogen content such as leachate cause various problems like eutrophication. In this study; the preliminary treatment of leachate which formed on the landfill site storing solid wastes of Samsun Metropolitan Municipality by MAP (Magnesium ammonium phosphate) precipitation was examined. For this purpose, optimization of the parameters that affecting the MAP precipitation was performed and the conditions for optimum removal efficiency were investigated. As a result of MAP precipitation, various mole ratios were tested with the aim of providing the best ammonia removal efficiency. The maximum ammonia removal was found to be 90.63% at pH 9.5 and at Mg:NH4:PO4 ratio of 4: 1: 2.2. At this conditions the ammonia concentration was decreased from 1792 mg/L to 168 mg/L. Experimental data were also evaluated and the regression equations of ammonia and COD removal were obtained using Minitab 16 statistical software.
Total file downloads: 3