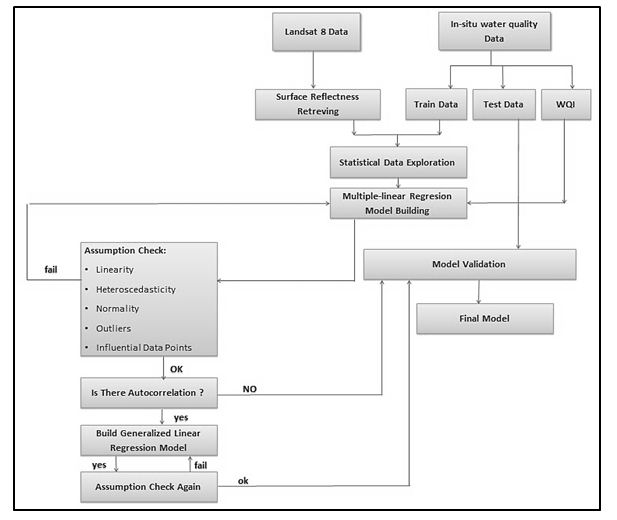
Since industrial and human activities have been developed in different ways in Iraq, water quality has been declining along the Hilla River, the only water resource for drinking water in the Hilla City, Iraq. In this research, The Weighted Arithmetic Water Quality Index (WQI) along the river was analysis using linear regression machine learning algorithm. Water quality parameters including Turbidity (Turb), Electric Conductivity (EC), Hydrogen Ions (pH), Total Suspended Solid (TSS), Chloride Ions (Cl), Sulfate Ions (SO4), Alkaline (ALK), Total Hardness (TH), Calcium Ions (Ca), Potassium Ions (k), Sodium Ions (Na), Magnesium Ions (Mg), and Total Dissolved Solid (TDS) were utilized to determine WQI from January 2016 to June 2021 depending on datasets from five sampling stations located along the river at the main city. It was noticed that the river WQI has a significant relationship with Turb only (positive proportion). This relationship between WQI and Turbidity in the river is limited to a WQI value of 220, Thus, two linear regression models were developed and validated: One for WQI values greater than 220 and another for the values less than 220. In addition, the results of this study showed that the Hilla River is severely polluted since WQI values are high. The best WQI and turbidity value were in 2018. However, in 2020 and 2021, there were some improvement in WQI and turbidity compared to 2019.
Total file downloads: 23