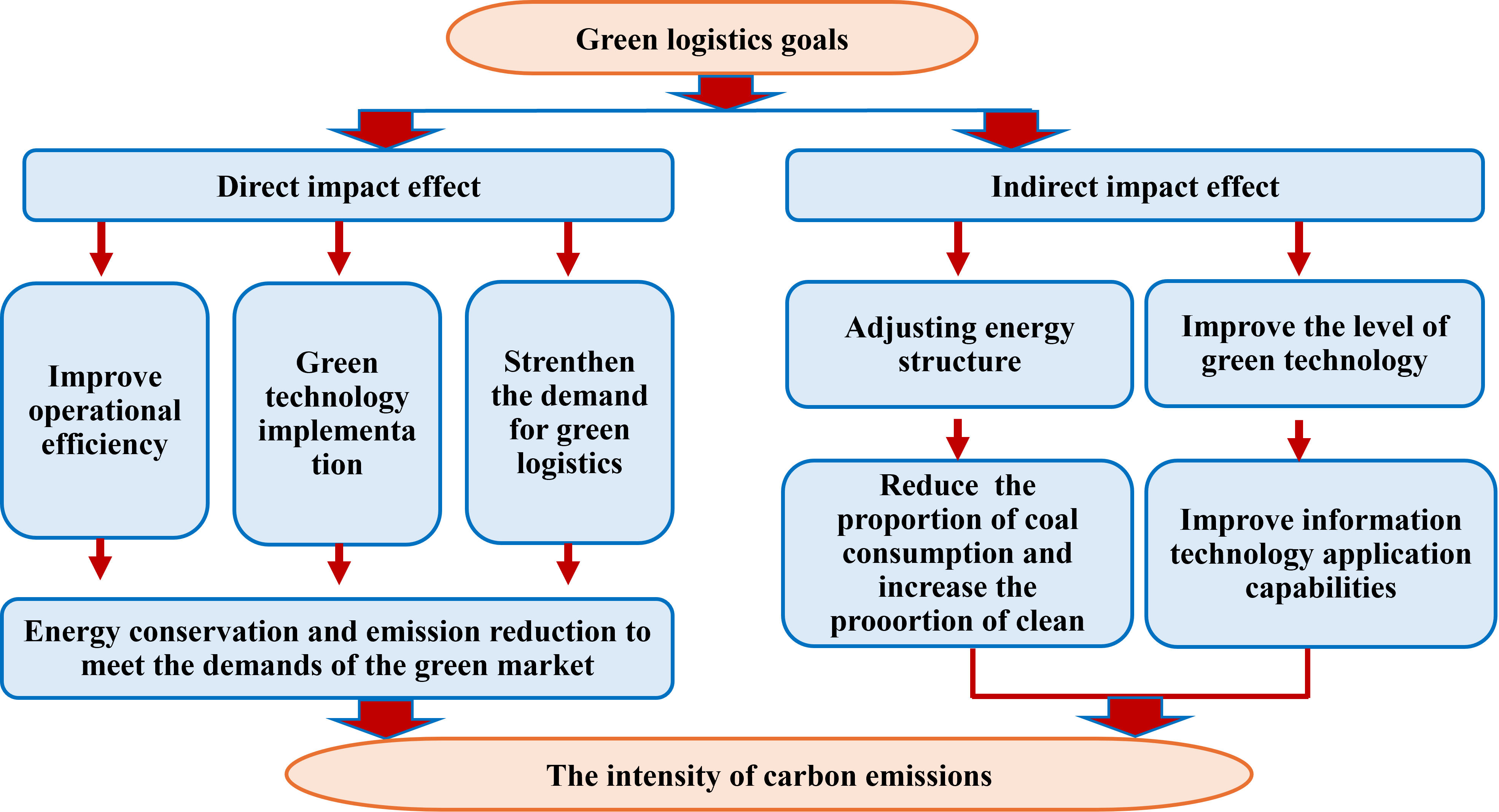
With the serious challenge of global climate change, the Chinese government has proposed the "dual carbon" goals. In this context, the importance of green logistics as an effective way to reduce emissions in the transportation industry is becoming more and more prominent. This paper aims to explore the impact of green logistics on the carbon emission intensity of the transportation industry, in order to provide reference for relevant policy formulation and industry practice. Based on quantitative research methods, the development level of green logistics in 30 provinces in China is quantified using the entropy method, followed by an examination of the impact of green logistics on carbon emission intensity within the transportation industry through the construction of a benchmark regression model. The findings suggest that implementing green logistics can significantly reduce carbon emission intensity, with energy structure optimization being one channel for achieving this reduction. Additionally, improving information technology levels through green logistics can also help lower carbon emissions. Regional heterogeneity tests indicate that green logistics has a significant inhibitory effect on carbon intensity in western and northeast regions, while it is not as effective in central and eastern regions. Therefore, China should continue developing green logistics while considering regional differences and industry characteristics to achieve low-carbon development within the transportation industry.
Total file downloads: 85