- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 60 Downloads
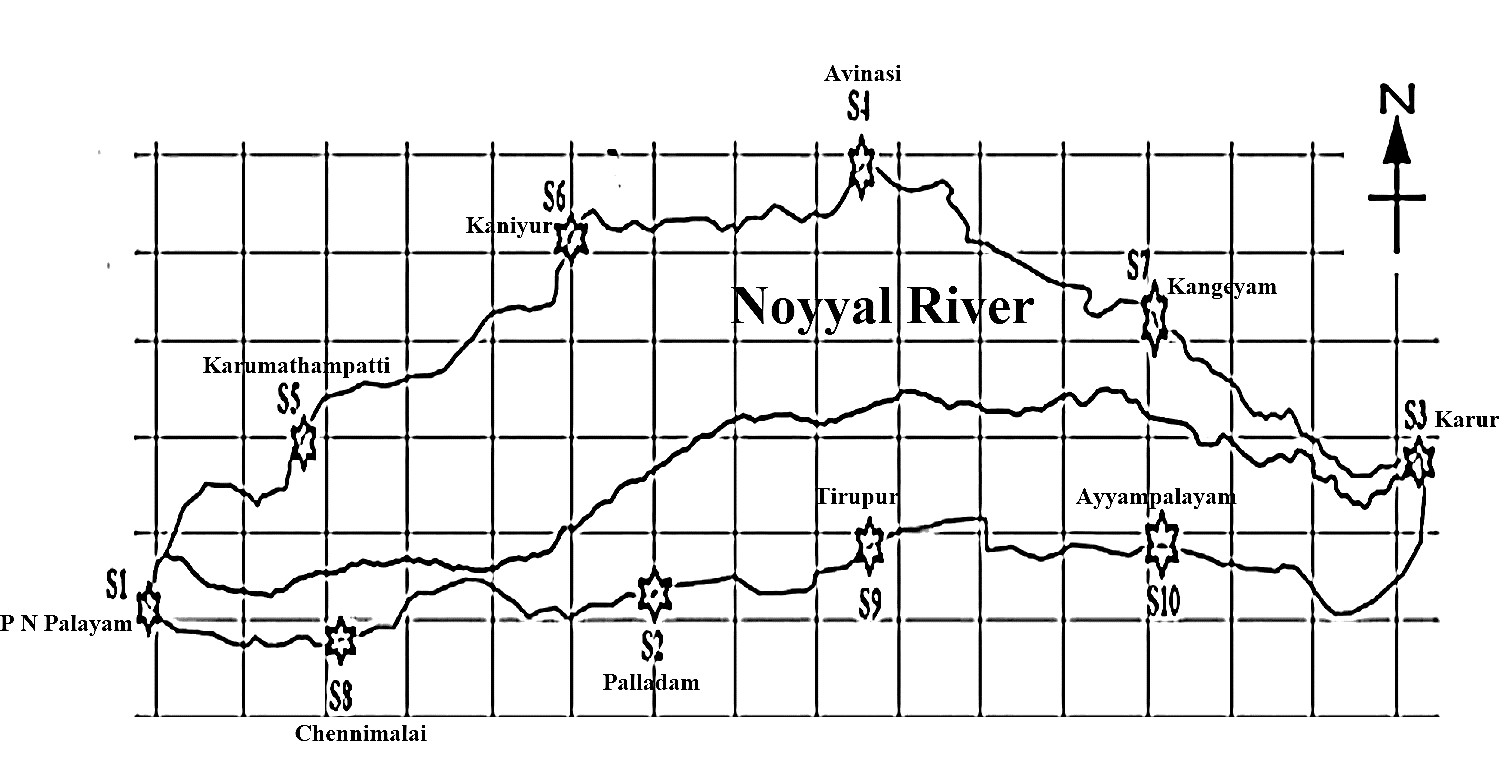
This study aimed to determine the extent of the water quality decrease in the Noyyal River in Tamilnadu by analyzing the seasonal change of water's physicochemical properties, identifying possible sources of pollution, and grouping the monitoring months based on shared characteristics. The measurements were taken during four different seasons. Forty percent of the water quality indices, including turbidity, DO concentration, EC, Cl concentration, TA, and COD in all seasons, were found to be outside the acceptable limits recommended by various agencies, according to the analytical data. A 95% confidence interval's worth of statistical analysis revealed that 52% of the contrasts differed significantly. Four factors accounted for 93.44% of the variation overall, according to the factor analysis, which showed the best fit between the parameters. The significant pollution loading, primarily attributed to toxicological chemicals and industrial discharge, was reflected in Total Dissolved Solids, Biochemical Oxygen Demand, Chemical Oxygen Demand, Electrical Conductivity, Turbidity, Dissolved Oxygen, and Chloride levels. Cluster analysis revealed a seasonal variation in surface water quality, indicating contamination from rainfall or other sources. Nevertheless, seasons did impact the levels of various physicochemical characteristics, with winter recording the highest pollution values. The Noyyal River's seasonal temperature change and increased rainfall were the causes of this self-refining tendency, which goes winter < summer < pre-winter < rainy season.