- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 13 Downloads
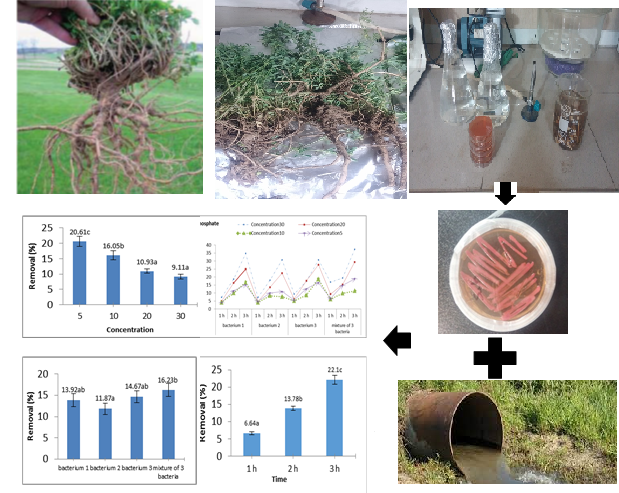
To conduct this experiment, rhizospheric bacteria were isolated from the root nodules of alfalfa plants (Medicago sativa) in the Khuzestan province during the spring season. For the molecular identification of superior isolates, DNA extraction and expression of 16S rDNA were performed. To investigate nitrate (NO3-) and phosphate (PO43-) removal, 120 mL vials were filled with 50 mL of laboratory wastewater containing specified concentrations of nitrate (25, 50, 100, and 200 mgL-1) and phosphate (5, 10, 20, and 30 mgL-1). The removal percentage was examined over 1, 2, and 3 hours. Results revealed that three rhizobial bacteria, including Sinorhizobium meliloti (bacterium 3) (Query ID= DQ-145546.1), Sinorhizobium medicae (bacterium 2) (Query ID= CP-000738.1), and Sinorhizobium meliloti (bacterium 1) (Query ID= CP 021215.1), were isolated and identified. The highest removal efficiency was recorded within 3 hours at 44.61%. With an increase in concentration, the removal efficiency decreased, reaching its lowest value (14.82%) at 200 mg L-1 compared to other concentrations (p < 0.05). Besides, the bacterial type or mixture did not significantly affect the nitrate removal percentage (p>0.05). At a concentration of 25 mg L-1, the highest removal percentage (63.08%) was measured in the presence of bacteria at 3 hours. Furthermore, the highest phosphate removal percentage was obtained at 37.4% at 5%, within 3 hours, and a mixture of 3 bacteria. Furthermore, the efficiency of the mixture of 3 bacteria was higher compared to bacterium 2 (p<0.05). Besides bacteria 1 and 3 with a removal percentage of 16.23% were ranked higher (p > 0.05). At higher concentrations and increased time, the nitrate and phosphate removal percentages exhibited a consistent and fluctuating trend, respectively (p > 0.05). Ribosome bacteria performed better in nitrate removal compared to phosphate (p > 0.05). Considering that wastewater from agricultural and industrial centers contains a mixture of nitrogenous and phosphorous substances, it appears that the use of a consortium of these bacteria with different characteristics and compatibilities enhances the efficiency of purification and removal of these parameters.